|
|
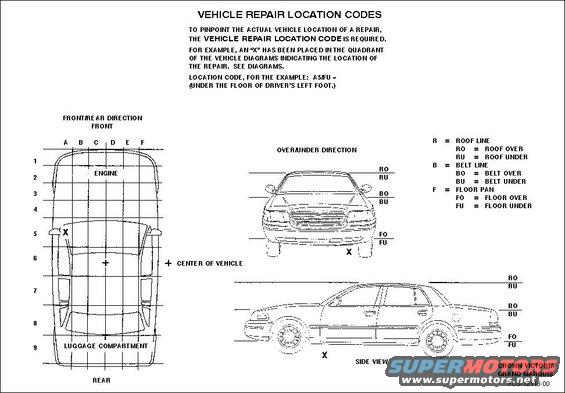 RepairLocationsCVGM.jpg | Hits: 7771 | Size: 42.51 KB | Posted on: 3/27/05 | Link to this image RepairLocationsCVGM.jpg | Hits: 7771 | Size: 42.51 KB | Posted on: 3/27/05 | Link to this image
Repair location grid for CV & GM
|
|
|
 RepairLocationsTC.jpg | Hits: 4621 | Size: 43.48 KB | Posted on: 3/27/05 | Link to this image RepairLocationsTC.jpg | Hits: 4621 | Size: 43.48 KB | Posted on: 3/27/05 | Link to this image
Repair location grid for TC
|
|
|
 1994 CrownVic frame.JPG | Hits: 10312 | Size: 73.99 KB | Posted on: 9/4/06 | Link to this image 1994 CrownVic frame.JPG | Hits: 10312 | Size: 73.99 KB | Posted on: 9/4/06 | Link to this image
1994 Crown Vic Frame Specs
|
|
|
 1994 CrownVic body.JPG | Hits: 5256 | Size: 50.14 KB | Posted on: 9/4/06 | Link to this image 1994 CrownVic body.JPG | Hits: 5256 | Size: 50.14 KB | Posted on: 9/4/06 | Link to this image
1994 Crown Vic Body Specs
|
|
|
 1998 CrownVic frame.JPG | Hits: 6419 | Size: 39.3 KB | Posted on: 9/4/06 | Link to this image 1998 CrownVic frame.JPG | Hits: 6419 | Size: 39.3 KB | Posted on: 9/4/06 | Link to this image
1998 Crown Vic Frame Specs
|
|
|
 1998 CrownVic body.JPG | Hits: 5697 | Size: 49.28 KB | Posted on: 9/4/06 | Link to this image 1998 CrownVic body.JPG | Hits: 5697 | Size: 49.28 KB | Posted on: 9/4/06 | Link to this image
1998 Crown Vic Body Specs
|
|
|
 2003 CrownVic frame.JPG | Hits: 6675 | Size: 43.13 KB | Posted on: 9/4/06 | Link to this image 2003 CrownVic frame.JPG | Hits: 6675 | Size: 43.13 KB | Posted on: 9/4/06 | Link to this image
2003 Crown Vic Frame Specs
|
|
|
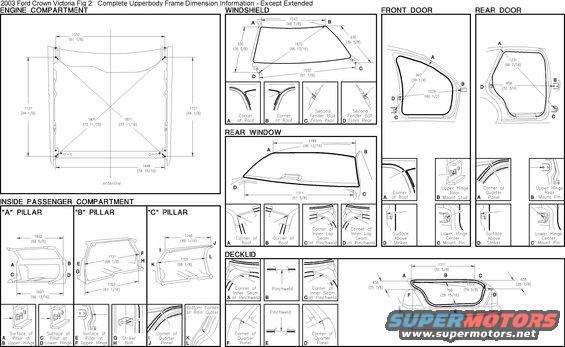 2003 CrownVic body.JPG | Hits: 4035 | Size: 46.62 KB | Posted on: 9/4/06 | Link to this image 2003 CrownVic body.JPG | Hits: 4035 | Size: 46.62 KB | Posted on: 9/4/06 | Link to this image
2003 Crown Vic Body Specs
|
|
|
 2005 CrownVic frame.JPG | Hits: 10006 | Size: 43.44 KB | Posted on: 9/4/06 | Link to this image 2005 CrownVic frame.JPG | Hits: 10006 | Size: 43.44 KB | Posted on: 9/4/06 | Link to this image
2005 Crown Vic Frame Specs
|
|
|
 2005 CrownVic body.JPG | Hits: 5372 | Size: 46.92 KB | Posted on: 9/4/06 | Link to this image 2005 CrownVic body.JPG | Hits: 5372 | Size: 46.92 KB | Posted on: 9/4/06 | Link to this image
2005 Crown Vic Body Specs
|
|
|
 BodyMounts92-97.jpg | Hits: 5653 | Size: 71.94 KB | Posted on: 11/28/05 | Link to this image BodyMounts92-97.jpg | Hits: 5653 | Size: 71.94 KB | Posted on: 11/28/05 | Link to this image
Body Mounts 97
|
|
|
Recommended Lubricants 1994 CV, GM, & TC
|
|
|
 EngineComponents94EVTM.jpg | Hits: 11065 | Size: 89.35 KB | Posted on: 3/20/05 | Link to this image EngineComponents94EVTM.jpg | Hits: 11065 | Size: 89.35 KB | Posted on: 3/20/05 | Link to this image
Engine Components 94 EVTM
|
|
|
 Engine ID Sticker.jpg | Hits: 6804 | Size: 25.61 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image Engine ID Sticker.jpg | Hits: 6804 | Size: 25.61 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image
|
|
|
General specifications for '93 4.6L modular engine
|
|
|
Torque specs for '93 4.6L modular engine
|
|
|
 Compression Pressures.jpg | Hits: 4914 | Size: 51.11 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image Compression Pressures.jpg | Hits: 4914 | Size: 51.11 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image
Compression Test
1. Ensure oil in crankcase is of the correct viscosity and at proper level and battery is properly charged. Operate vehicle until engine is at normal operating temperature. Turn ignition switch to the OFF position, then remove all spark plugs.
2. Set throttle plate in wide-open position.
3. Install a compression gauge such as Rotunda Compression Tester 059-00009 or equivalent in No. 1 cylinder.
4. Install an auxiliary starter switch in starting circuit. With ignition switch in the OFF position, and using auxiliary starter switch, crank engine at least five compression strokes and record highest reading. Note the approximate number of compression strokes required to obtain the highest reading.
5. Repeat test on each cylinder cranking the engine approximately the same number of compression strokes.
Test Conclusion:
The indicated compression pressures are considered within specification if the lowest reading cylinder is within 75 percent of the highest. Refer to the Compression Pressure Limit Chart.
If one or more cylinders read low, squirt approximately one tablespoon of XO-20W50-QR (ESR-M2C179-A) or equivalent engine oil on top of the pistons in the low reading cylinders. Repeat compression pressure check on these cylinders.
1. If compression improves considerably, piston rings are at fault.
2. If compression does not improve, valves are sticking or seating poorly.
3. If two adjacent cylinders indicate low compression pressures and squirting oil on pistons does not increase compression, cause may be a cylinder head gasket leak between cylinders. Engine oil and/or coolant in cylinders could result from this problem.
It is recommended the Compression Pressure Limit Chart be used when checking cylinder compression so that the lowest reading number is 75 percent of the highest reading.
|
|
|
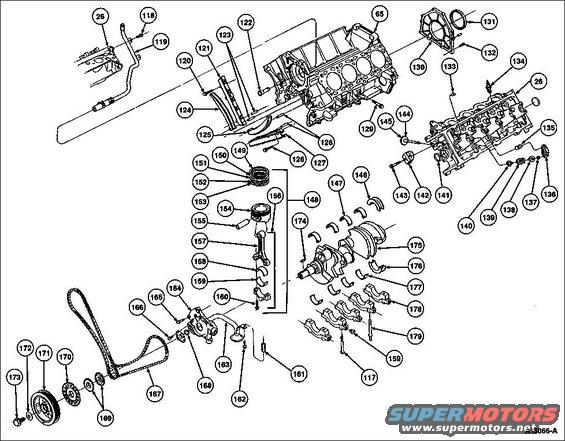
 Engine Exploded Complete.jpg | Hits: 26632 | Size: 104.47 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image Engine Exploded Complete.jpg | Hits: 26632 | Size: 104.47 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image
Exploded 4.6L 2V Complete
1 Bolt N806155-S2
2 Fuel Charging Wiring 9D930
3 Accelerator Cable Bracket 9723
4 Bolt N804394-S8M
5 Fuel Injection Supply Manifold 9F792
6 Fuel Injector (8 Req'd) 9F593
7 Nut N806178-S2
8 Water Hose Connection 8592
9 O-Ring 391107-S
10 Water Thermostat 8575
11 Intake Manifold Gasket 9461
12 Water Temperature Indicator Sender Unit 10884
13 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor 12A648
14 EGR Valve Tube to Manifold Connector 9F485
15 EGR Valve to Exhaust Manifold Tube 9D477
16 Bolt N804073-S8
17 EGR Valve 9D475
18 EGR Valve Gasket 9D476
19 Screw and Washer N806154-S2
20 Throttle Body 9E926
21 Throttle Body to Intake Manifold Gasket 9E936
22 Throttle Body Adapter 9A589
23 Bolt N806154-S2
24 Intake Manifold Upper Gasket 9H486
25 EGR Vacuum Regulator Bracket 9J472
26 Cylinder Head 6049
27 Bolt N804958-S2
28 Idle Air Control Valve 9F715
29 Bolt N806155-S2
30 IAC Valve Gasket 9F670
31 Bolt N806156-S2
32 Intake Manifold 9424
33 Core Plug 9A450
34 Positive Crankcase Ventilation Valve 6A666
35 Crankcase Ventilation Grommet 6A892
36 Bolt N806183-S2
37 Valve Cover Bolt or Stud Seal 6C518
38 Engine Front Cover Gasket 6020
39 Crankcase Vent Connector and Hose 6C324
40 A/C Compressor 19703
41 Bolt N806184-S2
42 Bolt N606502-S36
43 Ignition Coil 12029
44 Drive Belt Tensioner 6B209
45 Nut N804178-S2
46 Generator 10300
47 Screw and Washer N606676-S36
48 Generator Rear Mounting Bracket 10153
49 Bolt N806200-S2
50 Bolt N806155-S2
51 Crankshaft Position Sensor 6C315
52 Crankshaft Front Seal 6700
53 Bolt N806155-S2
54 Engine Front Cover 6019
55 Camshaft Position Sensor 6B288
56 Stud N806300-S2
57 Screw and Washer N806282-S2
58 Water Pump Pulley 8509
59 Bolt N806177-S2
60 Water Pump 8501
61 O-Ring 3Z728
62 Valve Cover Gasket 6584
63 Valve Cover (RH) 6582
64 Crankshaft Main Bearing Cap Bolt 6345
65 Cylinder Block 6010
66 Engine Rear Plate 7007
67 Flywheel 6375
68 Bolt N806168-S
69 Valve Cover Gasket 6584
70 Valve Cover (LH) 6582
71 Valve Cover Bolt or Stud Seal 6C515
72 Bolt N806183-S2
73 Fitting 6A648
74 Oil Filler Cap 6766
75 Stud N806356-S2
76 Valve Cover Bolt or Stud Seal 6C515
77 Head Gasket 6051
78 Dowel N806456-S
79 Oil Filter Mounting Insert 6890
80 Oil Filter Adapter Gasket 6840
81 Oil Filter Adapter 6881
82 Oil Pressure Switch 9278
83 Oil Pressure Sensor 9278
84 Stud N806514-S2
85 Bolt N806156-S2
86 Oil Bypass Filter 6714
87 Bolt N606523-S
88 Oil Pan Gasket 6710
89 Ignition Wires 12259
90 Bolt N806155-S2
91 Ignition Coil Bracket, LH 12A166
92 Ignition Wire Separator 12297
93 Stud W701624-S
94 Ignition Coil 12029
95 Bolt N606502-S36
96 Power Steering Pump Pulley 3A733
97 Power Steering Pump 3A674
98 O-Ring N806176-S2
99 Oil Pan Baffle 6687
100 Oil Pan 6675
101 Oil Pan Drain Plug Gasket 6734
102 Oil Pan Drain Plug 6730
103 Bolt (6 Req'd) W701240-S309
104 Nut W701575S
105 Exhaust Manifold 9430
106 Bolt N806139-S2
107 Washer N806164-S
108 Camshaft Sprocket 6256
109 Camshaft Sprocket Spacer 6265
110 Camshaft Bearing Cap (Front) 6B280
111 Camshaft Bearing Cap (Rear) 6B280
112 Bolt N806070-S
113 Camshaft 6250
114 Cylinder Head Bolt 6065
115 Oil Level Dipstick 6750
116 Bolt N806155-S2
117 Crankshaft Main Bearing Cap Bolt 6345
118 Bolt N806513-S2
119 Heater Water Hose 18472
120 Bolt N806070-S
121 Timing Chain Guide 6K297
122 Water Bypass Tube 8555
123 Dowel N806040-S
124 Timing Chain Tensioner Arm 6L253
125 Timing Chain Tensioner Arm 6L253
126 Bolt N806070-S
127 Timing Chain Guide 6K297
128 Dowel N806040-S
129 Crankshaft Main Bearing Cap Stud 6345
130 Crankshaft Rear Oil Seal Retainer 6335
131 Crankshaft Rear Oil Seal 6701
132 Bolt N806155-S2
133 Orifice and Strainer (Part of 6049)
134 Spark Plug 12405
135 Valve Tappet 6500
136 Rocker Arm 6564
137 Valve Spring Retainer Key 6518
138 Valve Spring Retainer 6514
139 Valve Spring 6513
140 Valve Stem Seal 6571
141 Core Plug N804811-S
142 Timing Chain Tensioner 6L266
143 Bolt N606543-S2
144 Intake Valve 6507
145 Exhaust Valve 6505
146 Crankshaft Thrust Washer 6334
147 Crankshaft Main Bearing 6333
148 Exhaust Manifold Gasket 9448
149 Piston Compression Ring 6150
150 Piston Compression Ring 6152
151 Oil Ring Rail 6159
152 Oil Ring Expander 6161
153 Oil Ring Rail 6159
154 Piston 6108
155 Piston Pin 6135
156 Bolt (2 Req'd)
157 Connecting Rod 6200
158 Connecting Rod Bearing 6211
159 Ignition Coil Bracket, RH 12A166
160 Connecting Rod Bolt 6214
161 Stud Spacer N806180- S
162 Bolt N605904-S
163 Oil Pump Screen Cover and Tube 6622
164 Oil Pump 6600
165 Bolt N606021-S
166 Bolt N605892-S2
167 Timing Chain 6268
168 O-Ring 87038-S96
169 Crankshaft Sprocket 6306
170 CKP Sensor Pulse Wheel 12A227
171 Crankshaft Pulley 6312
172 Crankshaft Pulley Retaining Washer 6378
173 Crankshaft Pulley Bolt 6A340
174 Woodruff Key N806201-S
175 Crankshaft 6303
176 Lower Crankshaft Thrust Main Bearing 6337
177 Lower Crankshaft Main Bearing (4 Req'd) 6333
178 Main Bearing Cap (5 Req'd, Part of 6010)
179 Crankshaft Main Bearing Cap Stud 6345
180 Belt Idler Pulley 8678
181 Stud Bolt
See also:

|
|
|
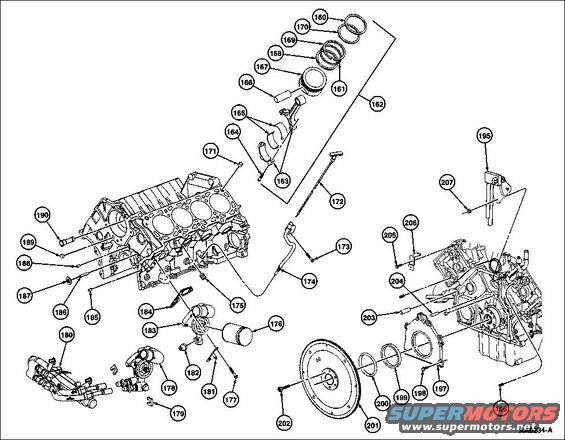
 Engine Exploded LongBlock.jpg | Hits: 11037 | Size: 67.92 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image Engine Exploded LongBlock.jpg | Hits: 11037 | Size: 67.92 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image
Exploded 4.6L 2V LongBlock
1 Bolt N806155-S2
2 Fuel Charging Wiring 9D930
3 Accelerator Cable Bracket 9723
4 Bolt N804394-S8M
5 Fuel Injection Supply Manifold 9F792
6 Fuel Injector (8 Req'd) 9F593
7 Nut N806178-S2
8 Water Hose Connection 8592
9 O-Ring 391107-S
10 Water Thermostat 8575
11 Intake Manifold Gasket 9461
12 Water Temperature Indicator Sender Unit 10884
13 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor 12A648
14 EGR Valve Tube to Manifold Connector 9F485
15 EGR Valve to Exhaust Manifold Tube 9D477
16 Bolt N804073-S8
17 EGR Valve 9D475
18 EGR Valve Gasket 9D476
19 Screw and Washer N806154-S2
20 Throttle Body 9E926
21 Throttle Body to Intake Manifold Gasket 9E936
22 Throttle Body Adapter 9A589
23 Bolt N806154-S2
24 Intake Manifold Upper Gasket 9H486
25 EGR Vacuum Regulator Bracket 9J472
26 Cylinder Head 6049
27 Bolt N804958-S2
28 Idle Air Control Valve 9F715
29 Bolt N806155-S2
30 IAC Valve Gasket 9F670
31 Bolt N806156-S2
32 Intake Manifold 9424
33 Core Plug 9A450
34 Positive Crankcase Ventilation Valve 6A666
35 Crankcase Ventilation Grommet 6A892
36 Bolt N806183-S2
37 Valve Cover Bolt or Stud Seal 6C518
38 Engine Front Cover Gasket 6020
39 Crankcase Vent Connector and Hose 6C324
40 A/C Compressor 19703
41 Bolt N806184-S2
42 Bolt N606502-S36
43 Ignition Coil 12029
44 Drive Belt Tensioner 6B209
45 Nut N804178-S2
46 Generator 10300
47 Screw and Washer N606676-S36
48 Generator Rear Mounting Bracket 10153
49 Bolt N806200-S2
50 Bolt N806155-S2
51 Crankshaft Position Sensor 6C315
52 Crankshaft Front Seal 6700
53 Bolt N806155-S2
54 Engine Front Cover 6019
55 Camshaft Position Sensor 6B288
56 Stud N806300-S2
57 Screw and Washer N806282-S2
58 Water Pump Pulley 8509
59 Bolt N806177-S2
60 Water Pump 8501
61 O-Ring 3Z728
62 Valve Cover Gasket 6584
63 Valve Cover (RH) 6582
64 Crankshaft Main Bearing Cap Bolt 6345
65 Cylinder Block 6010
66 Engine Rear Plate 7007
67 Flywheel 6375
68 Bolt N806168-S
69 Valve Cover Gasket 6584
70 Valve Cover (LH) 6582
71 Valve Cover Bolt or Stud Seal 6C515
72 Bolt N806183-S2
73 Fitting 6A648
74 Oil Filler Cap 6766
75 Stud N806356-S2
76 Valve Cover Bolt or Stud Seal 6C515
77 Head Gasket 6051
78 Dowel N806456-S
79 Oil Filter Mounting Insert 6890
80 Oil Filter Adapter Gasket 6840
81 Oil Filter Adapter 6881
82 Oil Pressure Switch 9278
83 Oil Pressure Sensor 9278
84 Stud N806514-S2
85 Bolt N806156-S2
86 Oil Bypass Filter 6714
87 Bolt N606523-S
88 Oil Pan Gasket 6710
89 Ignition Wires 12259
90 Bolt N806155-S2
91 Ignition Coil Bracket, LH 12A166
92 Ignition Wire Separator 12297
93 Stud W701624-S
94 Ignition Coil 12029
95 Bolt N606502-S36
96 Power Steering Pump Pulley 3A733
97 Power Steering Pump 3A674
98 O-Ring N806176-S2
99 Oil Pan Baffle 6687
100 Oil Pan 6675
101 Oil Pan Drain Plug Gasket 6734
102 Oil Pan Drain Plug 6730
103 Bolt (6 Req'd) W701240-S309
104 Nut W701575S
105 Exhaust Manifold 9430
106 Bolt N806139-S2
107 Washer N806164-S
108 Camshaft Sprocket 6256
109 Camshaft Sprocket Spacer 6265
110 Camshaft Bearing Cap (Front) 6B280
111 Camshaft Bearing Cap (Rear) 6B280
112 Bolt N806070-S
113 Camshaft 6250
114 Cylinder Head Bolt 6065
115 Oil Level Dipstick 6750
116 Bolt N806155-S2
117 Crankshaft Main Bearing Cap Bolt 6345
118 Bolt N806513-S2
119 Heater Water Hose 18472
120 Bolt N806070-S
121 Timing Chain Guide 6K297
122 Water Bypass Tube 8555
123 Dowel N806040-S
124 Timing Chain Tensioner Arm 6L253
125 Timing Chain Tensioner Arm 6L253
126 Bolt N806070-S
127 Timing Chain Guide 6K297
128 Dowel N806040-S
129 Crankshaft Main Bearing Cap Stud 6345
130 Crankshaft Rear Oil Seal Retainer 6335
131 Crankshaft Rear Oil Seal 6701
132 Bolt N806155-S2
133 Orifice and Strainer (Part of 6049)
134 Spark Plug 12405
135 Valve Tappet 6500
136 Rocker Arm 6564
137 Valve Spring Retainer Key 6518
138 Valve Spring Retainer 6514
139 Valve Spring 6513
140 Valve Stem Seal 6571
141 Core Plug N804811-S
142 Timing Chain Tensioner 6L266
143 Bolt N606543-S2
144 Intake Valve 6507
145 Exhaust Valve 6505
146 Crankshaft Thrust Washer 6334
147 Crankshaft Main Bearing 6333
148 Exhaust Manifold Gasket 9448
149 Piston Compression Ring 6150
150 Piston Compression Ring 6152
151 Oil Ring Rail 6159
152 Oil Ring Expander 6161
153 Oil Ring Rail 6159
154 Piston 6108
155 Piston Pin 6135
156 Bolt (2 Req'd)
157 Connecting Rod 6200
158 Connecting Rod Bearing 6211
159 Ignition Coil Bracket, RH 12A166
160 Connecting Rod Bolt 6214
161 Stud Spacer N806180- S
162 Bolt N605904-S
163 Oil Pump Screen Cover and Tube 6622
164 Oil Pump 6600
165 Bolt N606021-S
166 Bolt N605892-S2
167 Timing Chain 6268
168 O-Ring 87038-S96
169 Crankshaft Sprocket 6306
170 CKP Sensor Pulse Wheel 12A227
171 Crankshaft Pulley 6312
172 Crankshaft Pulley Retaining Washer 6378
173 Crankshaft Pulley Bolt 6A340
174 Woodruff Key N806201-S
175 Crankshaft 6303
176 Lower Crankshaft Thrust Main Bearing 6337
177 Lower Crankshaft Main Bearing (4 Req'd) 6333
178 Main Bearing Cap (5 Req'd, Part of 6010)
179 Crankshaft Main Bearing Cap Stud 6345
180 Belt Idler Pulley 8678
181 Stud Bolt
See also:

|
|
|
 Engine Exploded Internal 97.jpg | Hits: 5945 | Size: 59.38 KB | Posted on: 1/15/05 | Link to this image Engine Exploded Internal 97.jpg | Hits: 5945 | Size: 59.38 KB | Posted on: 1/15/05 | Link to this image
Exploded 4.6L
|
|
|
 Starter Exploded.jpg | Hits: 5152 | Size: 60.35 KB | Posted on: 3/19/05 | Link to this image Starter Exploded.jpg | Hits: 5152 | Size: 60.35 KB | Posted on: 3/19/05 | Link to this image
Starter Exploded
#2 is the solenoid, which operates lever #8
|
|
|
 Intake Sequence 93.jpg | Hits: 5104 | Size: 45.43 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image Intake Sequence 93.jpg | Hits: 5104 | Size: 45.43 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image
'93 Intake manifold tightening sequence
|
|
|
 Intake Components 4.6L.jpg | Hits: 5568 | Size: 79.94 KB | Posted on: 3/19/05 | Link to this image Intake Components 4.6L.jpg | Hits: 5568 | Size: 79.94 KB | Posted on: 3/19/05 | Link to this image
Intake Components
|
|
|
 Valve Spring Tools.jpg | Hits: 4696 | Size: 54.35 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image Valve Spring Tools.jpg | Hits: 4696 | Size: 54.35 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image
Valve Spring Tools
|
|
|
 Valve Stem Removal.jpg | Hits: 3919 | Size: 42.78 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image Valve Stem Removal.jpg | Hits: 3919 | Size: 42.78 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image
Valve Stem Removal
|
|
|
3. Install and seat camshaft cap cluster assemblies. Hand-start 14 bolts.
NOTE: Each camshaft cap cluster assembly is tightened individually.
4. Tighten camshaft cap cluster retaining bolts in sequence to 8-12 N-m (6.0-8.8 lb-ft).
5. Loosen 14 camshaft cap cluster retaining bolts approximately two turns or until head of bolt is free.
NOTE: Camshaft should turn freely with a slight drag.
6. Retighten all bolts in sequence to 8-12 N-m (6.0-8.8 lb-ft).
7. Check camshaft end play using Rotunda Dial Indicator with Bracketry 014-00282 or equivalent.
|
|
|
 Piston Cleaning.jpg | Hits: 3310 | Size: 41.07 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image Piston Cleaning.jpg | Hits: 3310 | Size: 41.07 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image
CAUTION: Do not use a caustic cleaning solution or a wire brush to clean pistons.
Remove deposits from the piston surfaces. Clean gum or varnish from the piston skirt, piston pins, and rings with solvent.
Clean the ring grooves with Piston Ring Groove Cleaner D81L-6002-D or equivalent, or a broken ring. Ensure oil ring slots (or holes) are clean.
Using a gasket scraper, carefully remove carbon deposits from piston dome.
|
|
|
 Piston Ring Side.jpg | Hits: 4598 | Size: 40.5 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image Piston Ring Side.jpg | Hits: 4598 | Size: 40.5 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image
6. Check side clearance of compression rings with Feeler Gauge D81L-4201-A or equivalent by inserting it between ring and its lower land. Gauge should slide freely around entire ring circumference without binding.
Ring side clearance:
Top ring: 0.040-0.090mm (0.0016-0.0035 inch)
2nd ring: 0.030-0.080mm (0.0012-0.0031 inch)
Service limit:
Top ring: 0.15mm max (0.006 inch max)
2nd ring: 0.15mm max (0.006 inch max)
If clearance is greater than service limit, replace piston ring. If clearance exceeds service limit, even with a new piston ring, replace piston.
|
|
|
The standard size pistons are color-coded green on the dome.
There are three sizes of the standard piston, color coded red, blue and yellow.
Piston diameter:
Red: 90.167-90.180mm (3.5499-3.5504 inch)
Blue: 90.180-90.193mm (3.5504-3.5509 inch)
Yellow: 90.193-90.206mm (3.5509-3.5514 inch)
|
|
|
 Piston Bore Measurement.jpg | Hits: 4923 | Size: 49.72 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image Piston Bore Measurement.jpg | Hits: 4923 | Size: 49.72 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image
Measure the cylinder bore and select the piston to ensure the proper clearance. When the bore diameter is in the lower one-third of the specified range, a red piston should be used. When the bore diameter is in the middle one-third, a blue piston should be used. When the bore diameter is in the upper one-third, a yellow piston should be used.
NOTE: Cylinder bore must be clean and dry, and engine block must remain at room temperature (21°C/70°F) for eight hours before taking cylinder measurements.
Measure the piston diameter to ensure the specified clearance is obtained. It may be necessary periodically to use another piston (within the same grade size) that is either slightly larger or smaller to achieve the specified clearance.
If none can be fitted, refinish the cylinder to provide the proper clearance for the piston.
When a piston has been fitted, mark it for assembly in the cylinder to which it was fitted.
If the taper, out-of-round and piston-to-cylinder bore clearance conditions of the cylinder bore are within specified limits, new piston rings will give satisfactory performance.
|
|
|
 Piston Bore Micrometer.jpg | Hits: 3157 | Size: 43 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image Piston Bore Micrometer.jpg | Hits: 3157 | Size: 43 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image
NOTE: After any refinishing operation, allow cylinder bore to cool, and ensure piston and bore are clean and dry before piston fit is checked.
1. Calculate size piston to be used by taking a cylinder bore check. Follow procedures outlined previously.
2. Select proper size piston to provide desired clearance. Measure piston diameter in-line with centerline of piston pin and at 90 degrees to piston pin axis.
3. Ensure piston and cylinder block are at room temperature, 21°C (70°F).
|
|
|
 Piston Ring Measurement.jpg | Hits: 4249 | Size: 52.25 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image Piston Ring Measurement.jpg | Hits: 4249 | Size: 52.25 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image
3. Subtract piston diameter measurement from cylinder bore diameter measurement. Standard piston to bore clearance is 0.20-0.046mm (0.0008-0.0018 inch).
Service limit: 0.070mm MAX (0.0028 inch MAX)
NOTE: The actual piston diameter is indicated on the top of all oversize pistons. If piston to bore clearance exceeds service limit, refinish cylinder to provide proper clearance for piston.
4. Insert piston ring into cylinder bore. Using a piston, push piston ring slightly beyond bottom of ring travel, 115mm (4.5 inch) from cylinder block deck face. Use caution to avoid damage to ring or cylinder bore.
5. Measure end gap of all piston rings with a feeler gauge.
Ring end gap:
Top ring: 0.23-0.49mm (0.009-0.019 inch)
2nd ring: 0.23-0.49mm (0.009-0.019 inch)
Oil ring rail: 0.25-0.77mm (0.010-0.030 inch)
Service limit:
Top ring: 1.00mm max (0.039 inch max)
2nd ring: 1.00mm max (0.039 inch max)
Oil ring rail: 1.25mm max (0.049 inch max)
If end gap is greater than service limit, replace piston ring. If end gap exceeds service limit, even with a new piston ring, rebore cylinder block.
|
|
|
NOTE: Clean cylinder head gasket surface with a toluene-based paint thinner or gasket remover. If gasket material remains on head after cleaning, use a 600 grit sandpaper to remove remaining material.
CAUTION: Do not use sandpaper coarser (lower number) than 600 grit.
|
|
|
 Head Bolt Sequence.jpg | Hits: 4639 | Size: 31.99 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image Head Bolt Sequence.jpg | Hits: 4639 | Size: 31.99 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image
Head Bolt Sequence
|
|
|
CAUTION: Failure to position crankshaft as shown will cause damage to pistons and/or valve train components.
NOTE: With crankshaft in this position, no piston will be at TDC.
|
|
|
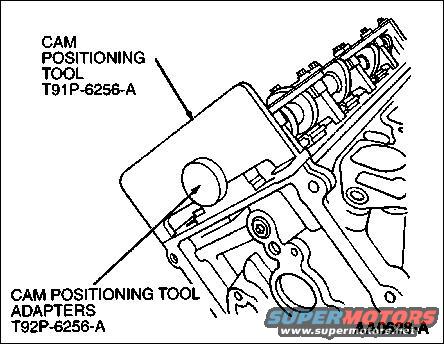 Cam Position Tools.jpg | Hits: 3635 | Size: 40.88 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image Cam Position Tools.jpg | Hits: 3635 | Size: 40.88 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image
Cam Position Tools
|
|
|
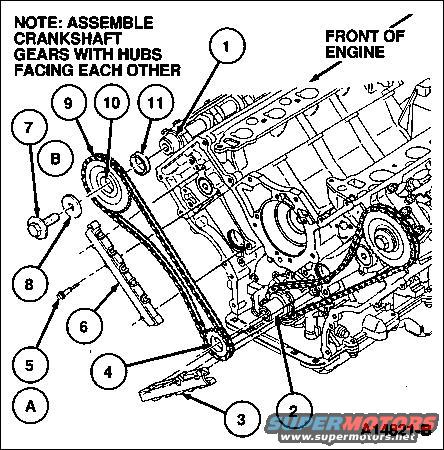 Chain Installation.jpg | Hits: 5347 | Size: 74.94 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image Chain Installation.jpg | Hits: 5347 | Size: 74.94 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image
Chain Installation
|
|
|
 Main Bearing Diagnosis.jpg | Hits: 4250 | Size: 68.53 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image Main Bearing Diagnosis.jpg | Hits: 4250 | Size: 68.53 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image
Main Bearing Diagnosis
|
|
|
 Crank Install 93.jpg | Hits: 3325 | Size: 74.48 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image Crank Install 93.jpg | Hits: 3325 | Size: 74.48 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image
Crank Install 93
|
|
|
Crank Position for #1 TDC
|
|
|
 Main Cap Install 93.jpg | Hits: 3329 | Size: 84.8 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image Main Cap Install 93.jpg | Hits: 3329 | Size: 84.8 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image
Main Cap Install 93
|
|
|
Remove air tube, fan & shroud, wiper assy, throttle cable, heater pipe fasteners from RH cyl head, blower resistor, & EGR pipe. Disconnect exhaust, drain oil, & lift engine.
|
|
|
 Oil Pan Sequence.jpg | Hits: 5083 | Size: 66.38 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image Oil Pan Sequence.jpg | Hits: 5083 | Size: 66.38 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image
Oil pan tightening sequence
|
|
|
 Oil Temp Range.jpg | Hits: 6850 | Size: 50.34 KB | Posted on: 12/4/04 | Link to this image Oil Temp Range.jpg | Hits: 6850 | Size: 50.34 KB | Posted on: 12/4/04 | Link to this image
Oil Temperature Ranges
TSB 02-1-9 ENGINE OIL - RECOMMENDED APPLICATIONS FOR SAE 5W-20 AND SAE 5W-30 MOTOR OILS - GASOLINE AND FLEXIBLE FUEL VEHICLES ONLY
Publication Date: JANUARY 14, 2002
FORD:
1992-2002 CROWN VICTORIA
1993-1994 TEMPO
1993-1997 THUNDERBIRD
1993-2002 ESCORT, MUSTANG, TAURUS
1995-2000 CONTOUR
1998-2002 ESCORT ZX2
2000-2002 FOCUS
1993-1996 BRONCO
1993-1997 AEROSTAR
1993-2002 E SERIES, F-150, RANGER
1995-2002 WINDSTAR
1997-1999 F-250 LD
1997-2001 EXPLORER
1997-2002 EXPEDITION
1999-2002 SUPER DUTY F SERIES, SUPER DUTY F-53 STRIPPED CHAS.
2000-2002 EXCURSION
2001-2002 ESCAPE
LINCOLN:
1991-2002 TOWN CAR
1993-1998 MARK VIII
1993-2002 CONTINENTAL
2000-2002 LS
1998-2002 NAVIGATOR
MERCURY:
1992-2002 GRAND MARQUIS
1993-1994 TOPAZ
1993-1997 COUGAR
1993-1999 TRACER
1993-2002 SABLE
1995-2000 MYSTIQUE
1999-2002 COUGAR
1997-2001 MOUNTAINEER
NOTE: PLEASE REFER TO THE VEHICLE APPLICATION LIST LATER IN THIS TSB FOR A COMPLETE LIST OF VEHICLES AFFECTED BY THIS TSB.
ISSUE: Ford Motor Company now recommends SAE 5W-20 viscosity grade for servicing most gasoline and flexible fueled vehicles.
ACTION: All 2001 and 2002 vehicles where SAE 5W-20 is specified should be serviced at the recommended oil change intervals using SAE 5W-20. This oil is an improved formulation to improve fuel economy. Testing has validated this viscosity grade can be used in many previous model year vehicles. It is recommended ALL vehicles on the following Vehicle Application Listing be service with SAE 5W-20.
All 2001-2002 vehicles other than those listed in the "Exception 2001 Vehicles" or "Exception 2002 Vehicles" chart are being filled with SAE 5W-20 motor oil at the factory and should also be serviced with SAE 5W-20 oil.
Vehicle Application Listing Approved For SAE 5W-20 Motor Oil
1993-1996 1.9L Escort/Tracer
1995-2000 2.0L Zetec Contour/Mystique
1999-2002 2.0L Cougar
1997-2002 2.0L Escort/Tracer
1998-2002 2.0L Escort ZX2
2000-2002 2.0L Focus
2001-2002 2.0L Escape
1993-1997 2.3L Ranger
1993-1994 2.3L Mustang
1993-1994 2.3L Tempo/Topaz
1998-2001 2.5L Ranger
1995-2000 2.5L Contour/Mystique
1999-2002 2.5L Cougar
2001-2002 3.0L 4V Escape
1996-2001 3.0L 4V Taurus/Sable
1993-2002 3.0L (Vulcan) Aerostar/Ranger, Taurus/Sable (Flexible Fuel and Gas)
1995-2000 3.0L (Vulcan) Windstar
1993-1994 3.0L (Vulcan) Tempo/Topaz
2000-2002 3.0L 4V Lincoln LS
1995-2002 3.8L Windstar
1993-1997 3.8L Taurus/Sable, Thunderbird/Cougar, Continental
1994-2002 3.8L Mustang
2002-2002 3.9L 4V Lincoln LS
1997-2002 4.2L (SPI) F-150 (under 8500 GVW only), E-Series
1996-2002 4.6L 2V Mustang
1992-2002 4.6L Crown Victoria/Grand Marquis
1991-2002 4.6L Town Car
1994-1997 4.6L 2V Thunderbird/Cougar
1996-2002 4.6L 4V Mustang Cobra
1995-2002 4.6L 4V Continental
1993-1998 4.6L 4V Mark VIII
1997-2002 4.6L 2V Triton F-150/250 (under 8500 GVW only), E-Series, Expedition
1993-1999 4.9L E-Series, F-Series
1993-1995 5.0L Mustang/Mustang Cobra
1993-1993 5.0L Thunderbird/Cougar
1997-2001 5.0L Explorer/Mountaineer
1993-1996 5.0L E-Series, F-Series, Bronco
2000-2002 5.4L Excursion
1998-2002 5.4L 2V/4V Navigator
1997-2002 5.4L 2V F-150/250 (under 8500 GVW only), Expedition, E-Series, E-350 Chassis/RV/Cutaway
1993-1997 5.8L F-Series, Bronco
1993-1996 5.8L E-Series
2000-2002 6.8L Excursion
1997-2002 6.8L E-Series, E-350 Chassis/RV/Cutaway
1999-2002 6.8L Super Duty F-Series 250 HD/350/450/550 Motorhome
1993-1998 7.5L All Vehicles
NOTE: FOR 1993 THROUGH 1998 MODEL YEAR FFV USE XO-10W30-FFV.
NOTE: THE "EXCEPTION 2001-2002 VEHICLES" SHOULD BE SERVICED WITH SAE 5W-30 MOTOR OIL.
Exception 2001 Vehicles
3.3L Villager
3.9L Lincoln LS
4.0L Ranger, Explorer/Mountaineer, Explorer Sport, and Explorer Sport Trac
Exception 2002 Vehicles
2.0L HP Zetec SVT Focus
3.3L Villager
4.0L Ranger, Explorer/Mountaineer, Explorer Sport, and Explorer Sport Trac
NOTE: IF VEHICLE IS NOT LISTED IN THIS APPLICATION, SAE 5W-30 OIL IS RECOMMENDED. REFER TO TSB 99-8-16.
PART NUMBER PART NAME
XO-5W20-QSP SAE 5W-20 Motor Oil - Quart (USA)
CXO-5W20-LSP12 SAE 5W-20 Motor Oil - Litre (Canada)
XO-5W20-5QSP SAE 5W-20 Motor Oil - 5 Quart Jug (USA)
XO-5W20-DSP SAE 5W-20 Motor Oil - 55 Gallon Drum (USA)
CXO-5W20-DBSP SAE 5W-20 Motor Oil - 205 Litre Drum (Canada)
OTHER APPLICABLE ARTICLES: 99-8-16
SUPERSEDES: 01-4-7
|
|
|
Oil flow for 4.6L modular engine
|
|
|
 Oil Cooler HPP97.jpg | Hits: 5886 | Size: 57.98 KB | Posted on: 1/15/05 | Link to this image Oil Cooler HPP97.jpg | Hits: 5886 | Size: 57.98 KB | Posted on: 1/15/05 | Link to this image
Oil Cooler
|
|
|
Coolant Flow for 4.6L modular engine Note that: before the t-stat opens (engine cold), ALL of the water pump's pressure goes thru the heater core. So the high coolant flow at that time will self-bleed any air out of the heater core, but it can also overpressure the core, which is why Ford is now adding a restrictor to many vehicles. See the TSB in this caption:  Smallblock V8 
|
|
|
The pulley bolts are tightened the same as the WP bolts.
|
|
|
 Trans fluid app chart.jpg | Hits: 3453 | Size: 91.02 KB | Posted on: 12/4/04 | Link to this image Trans fluid app chart.jpg | Hits: 3453 | Size: 91.02 KB | Posted on: 12/4/04 | Link to this image
Trans Fluid App Chart
|
|
|
 TorqueConverter92.jpg | Hits: 6495 | Size: 84.43 KB | Posted on: 5/8/05 | Link to this image TorqueConverter92.jpg | Hits: 6495 | Size: 84.43 KB | Posted on: 5/8/05 | Link to this image
AOD Components (2WD/RWD)  .  . 
|
|
|
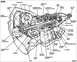
 TorqueConverter94.jpg | Hits: 4029 | Size: 53.74 KB | Posted on: 5/8/05 | Link to this image TorqueConverter94.jpg | Hits: 4029 | Size: 53.74 KB | Posted on: 5/8/05 | Link to this image
Torque Converter for AODE
 . 
|
|
|
 AODE Valve Body Installation.jpg | Hits: 5239 | Size: 45.17 KB | Posted on: 4/3/05 | Link to this image AODE Valve Body Installation.jpg | Hits: 5239 | Size: 45.17 KB | Posted on: 4/3/05 | Link to this image
Valve Body Torque Sequence
1. Tighten the 25 retaining bolts to case to 9-11 N-m (80-100 lb-in).
2. Retighten the following bolts to the specification indicated and in sequence as indicated by the illustration:
> 2 M8X1.25X46mm guide pin bolts to 22-26 N-m (190-230 lb-in).
> 4 M6X1.0X18mm cover plate bolts to 9-11 N-m (80-100 lb-in).
> 12 M6X1.0X52mm cover plate bolts to 11-15 N-m (100-130 lb-in)
|
|
|
 4R70WComponents98.jpg | Hits: 23778 | Size: 86.17 KB | Posted on: 4/3/05 | Link to this image 4R70WComponents98.jpg | Hits: 23778 | Size: 86.17 KB | Posted on: 4/3/05 | Link to this image
4R70W Components
|
|
|
 TorqueConverter00.jpg | Hits: 17374 | Size: 63.97 KB | Posted on: 5/7/05 | Link to this image TorqueConverter00.jpg | Hits: 17374 | Size: 63.97 KB | Posted on: 5/7/05 | Link to this image
Torque Converter Cutaway 4R70W
Torque Converter Operation Test
This test verifies that the torque converter clutch control system and the torque converter are operating correctly.
1. Carry out Quick Test with scan tool. For additional information, refer to the Powertrain Control/Emissions Diagnosis manual (PCED). Check for DTCs.
2. Connect a tachometer to the engine.
3. Bring the engine to normal operating temperature by driving the vehicle at highway speeds for approximately 15 minutes in (D) position.
4. After normal operating temperature is reached, maintain a constant vehicle speed of about 80 km/h (50 mph) and tap brake pedal with the left foot.
5. Engine rpm should increase when brake pedal is tapped, and decrease about five seconds after pedal is released. If this does not occur, see torque converter operation concerns.
6. If the vehicle stalls in (D) or manual 2 at idle with vehicle at a stop, move the transmission range selector lever to manual 1 position. If the vehicle stalls, see torque converter operation concerns.
7. If the vehicle exhibits a vibration during the road test complete the Road Test Evaluation Form. This form will aid the technician in determining the source of the vibration.
Note: The following is a list of common vehicle concerns that have been misdiagnosed as torque converter clutch shudder. For diagnosis of the following items, refer to the appropriate sections of the workshop manual and the Powertrain Control/Emissions Diagnosis manual (PCED).
> Spark plugs - check for cracks, high resistance or broken insulators.
> Plug wires.
> Fuel injector - filter may be plugged.
> Fuel contamination - engine runs poorly.
> EGR valve - valve may let in too much exhaust gas and cause engine to run lean.
> Vacuum leak - engine will not get correct air/fuel mixture.
> MAP/MAF sensor - improper air/fuel mixture.
> HO2S sensor - too rich/lean air/fuel mixture.
> Fuel pressure - may be too low.
> Engine mounts -loose/damaged mounts can cause vibration concerns.
> Axle joints - check for vibration.
Abbreviated Road Test Evaluation Form
If the shudder occurs a) during the 3-4 or 4-3 shift at HEAVY throttle, or b) at 40mph in 2, OD OFF, and OD, or c) at the same RPM in every gear, or d) coasting, cruising, or in R, or e) during extended light braking, then it is NOT TC clutch shudder.
|
|
|
 4R70WDisassembled98.jpg | Hits: 15331 | Size: 73.52 KB | Posted on: 4/3/05 | Link to this image 4R70WDisassembled98.jpg | Hits: 15331 | Size: 73.52 KB | Posted on: 4/3/05 | Link to this image
Exploded 4R70W
1 7902 Converter Assy
2 87650-S2 Plug - Converter Drain - 1/8-27 Dryseal
3 7A103 Pump Assy - Front
4 7A248 Seal Assy - Front Pump
5 7A248 Seal - Front Pump
6 7B258 Bushing - Front Pump
7 N605789-S100Bolt - M8-1.25 X 35 Hex Head (7-Attach 7A103 to 7005)
8 7A106 Body Assy - Front Pump (Part of 7A103)
9 7A136 Gasket - Front Pump
10 7H169 Gear - Pump Inner Gerotor (Part of 7A103)
11 7H169 Gear - Pump Outer Gerotor (Part of 7A103)
12 7A108 Support Assy - Front Pump
13 N605787-S Bolt - M8-1.25 X 25 Hex Flg Head (5-Attach 7A108 to 7A103)
14 7D014 Washer - Front Pump Support Thrust -Select Fit No.1
15 7D020 Seal - Reverse Clutch Cylinder (2 Required)
16 7D019 Seal - Forward Clutch Cylinder (2 Required)
17 7F225 Seal - Intermediate Clutch Piston - Inner
18 7F224 Seal - Intermediate Clutch Piston - Outer
19 7E005 Piston Kit - Intermediate Clutch
20 7B442 Plate - Intermediate Clutch External Spline (Select Fit) (Steel)
21 7B164 Plate Assy - Intermediate Clutch Internal Spline (Friction)
22 7B066 Plate - Intermediate Clutch Pressure
23 7F196 Band Assy - Overdrive
24 391267-S Ring - 3-21/64 Retains Type SU External (Retains 7F262 to 7F215)
25 7F271 Clutch Assy - Intermediate One-Way Clutch
26 7D044 Drum Assy - Reverse Clutch
27 7D403 Seal - Reverse Clutch Piston - Outer
28 7D402 Piston Assy - Reverse Clutch
29 7D404 Seal Reverse Clutch Piston - Inner
30 7D256 Ring - Reverse Clutch Piston Pressure
31 7B070 Spring - Reverse Clutch Piston Return
32 7A577 Spring - Reverse Clutch Piston Spring
33 7B066 Plate - Reverse Clutch Front Pressure
34 7B164 Plate - Reverse Clutch Internal Spline (Friction)
35 7B442 Plate - Reverse Clutch External Spline (Steel)
36 7B066 Plate - Reverse Clutch Rear Pressure
37 7B497 Seal - Input Shaft (2 Required)
38 7D483 Retainer - Reverse Clutch Pressure Plate - (Select Fit)
39 7A166 Bearing and Race Assy - Forward Clutch No.2
40 7F207 Cylinder and Input Shaft Assy - Forward Clutch
41 7A548 Seal - Forward Clutch Piston - Outer
42 7C099 Seal - Forward Clutch Piston - Inner
43 7A262 Piston - Forward Clutch
44 7A480 Spring - Forward Clutch Piston Return
45 7A527 Retainer Return Spring - Forward Clutch
46 388099-S Snap Ring - Retaining - 1-59/64 (Retains 7A529 in 7F207)
47 7E085 Spring - Rear Clutch Pressure Plate
48 7B442 Plate - Forward Clutch External Spline (Steel)
49 7B164 Plate - Forward Clutch Internal Spline (Friction)
50 7B066 Plate - Forward Clutch Pressure
51 7D483 Snap Ring - Retaining (Select Fit)
52 7F231 Bearing and Race Assy - Forward Clutch - Front No.3
53 7B067 Hub - Forward Clutch
54 7F351 Shaft - Intermediate Stub
55 7C096 Bearing and Race Assy - Forward Clutch Hub No.4
56 7A019 Gear Assy - Reverse Sun
57 7F244 Bearing and Race Assy - Forward Clutch Sun Gear No.5
58 388501-S Retaining Ring - Center Support - 7-7/92
59 7A399 Gear Assy - Forward Clutch Sun
60 7F277 Spring - Case to Planet Support
61 7A130 Support Assy - Planetary Gear
62 7A089 OWC Cage Spring and Roller Assy - Planetary
63 7A398 Planetary Assy
64 7D095 Band Assy - Reverse
65 377437-S Retaining Ring - 0.58 Thick (Locates Reverse Band During Assy)
66 7F236 Hub - Direct Clutch
67 7F243 Bearing and Race Assy - Direct Clutch Inner No.7
68 7F237 Support - Direct Clutch Inner Bearing
69 7D483 Retaining Ring - Direct Clutch Pressure Plate (Select Fit)
70 7B066 Plate - Direct Clutch Pressure
71 7B164 Plate - Direct Clutch Internal Spline (Friction)
72 7B442 Plate - Direct Clutch External Spline (Steel)
73 388104-S Retaining Ring - 1-19/32 (Retains 7F235 to 7F283)
74 7F235 Retainer and Spring Assy - Direct Clutch
75 7A262 Piston Assy - Direct Clutch
76 7C099 Seal - Direct Clutch Piston - Inner
77 7A233 Seal - Direct Clutch Piston - Outer
78 7A153 Gear - Output Shaft Ring
79 7F283 Cylinder Assy - Direct Clutch
80 7F274 Seal - Output Shaft Small – Direct Clutch (2 Required)
81 7F240 Bearing and Race Assy - Direct Clutch Outer No.8
82 7060 Shaft Assy - Output
83 7F273 Seal - Output to Case Shaft Large (3 Required)
84 87054-S94 Seal - O-Ring (Piloted Output Shaft Only)
85 7D164 Hub - Output Shaft
86 97713-SSnap Ring - 1-13/16 Retaining (Retains 7D164 to 7060)
87 7C122 Snap Ring - Retaining (Retains 7D164 to 7A153)
88 7025 Bushing - Rear Case
89 7F242 Bearing and Race Assy - Case Rear No.9
90 7005 Case Assy
91 7086 Gasket - Extension
92 N803747-S1101 Bolt - M8-1.25 X 30 (6-Attach 7A039 to 7005)
93 7A039 Extension Assy
94 7A034 Bushing - Extension Housing
95 7052 Seal Assy - Extension Housing
96 390318-S100 Pipe Plug - 1/8-27 Dryseal Tapered (5 Required)
97 7F295 Pin - Overdrive Band Anchor
98 388142-S Pin - Reverse Band Anchor (Part of 7005)
99 7034 Vent Assy - Case
100 N605771-S427Bolt - M6-1.0 X 14 Hex Flg Head (Attaches Output Shaft Speed Sensor to Case)
101 7H103 Sensor Assy - Transmission Output Shaft Speed
102 7Z101 Seal - 14.0 X 1.78 O-Ring (2 Required)
103 N806933-S102Bolt and Washer Assy - M6-1.0 X 25MM (2 -Attach 7F293 to 7005)
104 7A247 Sensor - Transmission Range
105 7A256 Lever Assy - Manual Control
106 7B498 Seal Assy - Manual Control Lever
107 373907-S2 Nut - 1/4 Spring (Retains Identification Tag to 7000)
108 7B148 Tag - Identification (Part of 7005)
109 7D273 Connector Assy - Fluid Tube (2 Required)
110 7N171 Plug - Converter Housing Access
111 7E242 Screen Assy - Fluid
112 7B210 Pin - Manual Lever Shaft Retainer
113 7Z383 Seal - 0.426 X 0.070 O-Ring
114 7Z101 Seal - 14.0 X 1.78 O-Ring
115 7G383 Solenoid Valve - Transmission Pressure Control
116 7A441 Pawl - Parking Pawl
117 7D071 Shaft - Parking Pawl
118 7D419 Cup - Park Rod Guide (Part of 7A039)
119 7D070 Spring - Parking Pawl Return
120 7A232 Rod Assy - Park Pawl Actuating
121 7A115 Lever Assy - Manual Valve Detent Lever
122 N800287-S536Nut - M14 X 1.5 Hex - Intermediate Detent Lever (Attaches 7A115 to 7A256)
123 7H188 Piston Assy - Overdrive Servo
124 7F201 Spring - Overdrive Servo Piston
125 7F203 Rod - Overdrive Servo Actuating (Part of 7H188 )
126 7H179 Washer - Backup Overdrive Servo (Part of 7H188 )
127 7G277 Spring - Overdrive Cushion Spring (Part of 7H188 )
128 7F200 Piston Assy - Overdrive Servo (Part of 7H188 )
129 97411-SRing - Retaining (Part of 7H188 )
130 7F411 Sleeve Assy - Overdrive Servo (Part of 7H188 )
131 7384 Ring - 2.85 Retaining Type TVP "H" Internal (Retains 7H188 to 7005)
132 7D031 Spring - Reverse Band Servo Piston
133 7D189 Piston Assy - Reverse Band Servo
134 7D036 Cover Assy - Reverse Band Servo Piston
135 388215-S100 Retaining Ring - Internal - 3-13/16
136 7H292 Piston Seal - 2-3 Accumulator (Bonded Seals)
137 7F285 Spring - 2-3 Shift Accumulator Piston
138 7B264 Retainer - 2-3 Shift Accumulator Spring
139 7F284 Spring - 1-2 Shift Accumulator
140 7F251 Piston Assembly - 1-2 Shift Accumulator
141 7F284 Spring - 1-2 Shift Accumulator
142 7H300 Cover and Seal Assy - 1-2 Accumulator
143 7384 Ring - 2-1/16 Retaining Type HU Internal (Retains 7H300 to 7005)
144 N807178-S1000 Bolt - M6-1.0 X 16 Hex Head (12-Attach Reinforcing Plate to Valve Body)
145 7F282 Plate - Valve Body Reinforcing (Part of 7A100)
146 7C155 Gasket - Valve Body Separator - Upper
147 7A008 Plate - Control Valve Body Separator (Part of 7A100)
148 7D100 Gasket - Valve Body Separating - Lower
149 7H171 Valve - Converter Drainback
150 7A091 Body Assy - Main Control
151 7H173 Gasket - Valve Body Cover Plate
152 7C034 Plate - Valve Body Cover (Part of 7A100)
153 N807178-S1000 Bolt - M6-1.0 X 18 Hex Head (11-Attach 7C034 to 7A100)(Part of 7A100)
154 7A100 Control Assy - Main
155 7A098 Filter and Seal Assy - Fluid
156 7A191 Gasket - Transmission Pan
157 7A194 Pan - Transmission
158 N605785-S427Bolt - M8-1.25 X 18 Hex Flg Head (14-Attach 7A194 to 7005)
159 7L027 Magnet - Ceramic Case (Part of 7A194)
160 N808947-S1300 Bolt - M8-1.25 X 46 Hex Shldr Pilot (2 -Attach 7C034 to 7A100)
161 N807179-S1000 Bolt - M6-1.0 X 52 Hex Flg Head (12 -Attach 7A100 to 7005)
162 7H111 Retainer - Solenoid
163 7E195 Ball - 1/4 Diameter Coast Booster Valve Shuttle (8 Required)
164 7H187 Screen - Solenoid Pressure Supply
165 N606022-S1000 Bolt - M6-1.0 X 40 Hex Flg Head (13 -Attach 7A100 to 7005)
166 7E332 Spring Assy - Manual Valve Detent
167 7Z276 Seal - 0.864 X 0.070 O-Ring (2 Required)
168 7G276 Bulkhead Assy - Wiring Connector
169 7G276 Bulkhead Assy - Connector (Molded Lead Frame)
170 7Z484 Seal - 6.07 x 1.70 O-Ring (2 Required)
171 7G484 Solenoid Valve - Transmission Shift
172 7G136 Solenoid Valve - Transmission Torque Converter Clutch
173 N807178-S1000 Bolt - M6-1.0 X 16 Hex Head (Retains 7G136 & 7G484 to 7A100)
174 7Z136 Seal - 0.489 x 0.070 O-Ring
175 7Z484 Seal - 0.176 x 0.070 O-Ring
A --Intermediate Clutch Assy
B --Intermediate One-Way Clutch
C --Reverse Clutch Assy
D --Forward Clutch Assy
E --Direct Clutch Assy
|
|
|
Bushings 4R70W
1 7D014 Pump Assy Thrust Washer (Select Fit)
2 7A166 Forward Clutch Bearing and Race Assy
3 7F231 Forward Clutch Front Bearing and Race Assy
4 7F244 Forward Clutch Sun Gear Bearing and Race Assy
5 7F244 Forward Clutch Sun Gear Bearing and Race Assy
6 7F241 Planetary Bearing and Race Assy
7 7F243 Direct Clutch Inner Bearing and Race Assy
8 7F237 Direct Clutch Inner Bearing Support No. 7
9 7F240 Direct Clutch Outer Bearing and Race Assy
10 7F242 Outer Race Bearing and Race Assy
11 7A034 Extension Bushing
12 7025 Case Bushing
13 7B233 Output Shaft Bushing
14 7B375 Rear Planetary Carrier Bushing
15 7F209 Forward Clutch Sun Gear Bushing
16 7N193 Reverse Clutch Sun Gear Bushing
17 7B374Front Carrier Bushing
18 7A132Planetary Support Bushing
19 -- Reverse Clutch Drum Rear Bushing
20 7B261Front Pump Support Bushing
21 7F217Reverse Clutch Drum Front Bushing
22 7B258Front Pump Bushing
23 7B261Front Pump Support Bushing
|
|
|
 4R70WValveBodyInstallation.jpg | Hits: 5694 | Size: 53.52 KB | Posted on: 4/3/05 | Link to this image 4R70WValveBodyInstallation.jpg | Hits: 5694 | Size: 53.52 KB | Posted on: 4/3/05 | Link to this image
Valve Body Torque Sequence
|
|
|
4R70W Shifter Adjustment
23. From inside the vehicle, place the gearshift lever in the DRIVE or OVERDRIVE position. Hang a three-pound weight on the gearshift lever.
24. Raise the vehicle.
25. Remove the shift cable from the transmission lever ball stud. Pull down on the lock tab on the shift cable body. Position the gearshift lever in the DRIVE or OVERDRIVE position (three detents from front-most lever position, with the first position counted as one). Connect the cable end fitting to the transmission lever ball stud. Push up on the lock tab to lock the cable in the correctly adjusted position.
26. Lower the vehicle.
27. Remove the three-pound weight.
|
|
|
 4R70WControls98.jpg | Hits: 5473 | Size: 80.81 KB | Posted on: 4/3/05 | Link to this image 4R70WControls98.jpg | Hits: 5473 | Size: 80.81 KB | Posted on: 4/3/05 | Link to this image
Trans Electronic Controls
All of these influence the transmission's behavior.
|
|
|
 PSConnections.jpg | Hits: 11483 | Size: 66.77 KB | Posted on: 1/15/05 | Link to this image PSConnections.jpg | Hits: 11483 | Size: 66.77 KB | Posted on: 1/15/05 | Link to this image
Power Steering Connections
|
|
|
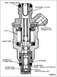
 Fuel Injector Types.jpg | Hits: 3865 | Size: 29.84 KB | Posted on: 3/19/05 | Link to this image Fuel Injector Types.jpg | Hits: 3865 | Size: 29.84 KB | Posted on: 3/19/05 | Link to this image
Fuel Injector Types
See also:
 .  .  . 
|
|
|
 Fuel Injector Cutaway.jpg | Hits: 11653 | Size: 62.61 KB | Posted on: 3/19/05 | Link to this image Fuel Injector Cutaway.jpg | Hits: 11653 | Size: 62.61 KB | Posted on: 3/19/05 | Link to this image
Fuel Injector Cutaway The fuel injector nozzles are electro-mechanical devices which both meter and atomize fuel delivered to the engine. The injectors are mounted in the lower intake manifold and are positioned so that their tips direct fuel just ahead of the engine intake valves. The injector bodies consist of a solenoid, needle and valve assembly and a director/metering plate. An electrical control signal from the Electronic Engine Control unit activates the injector solenoid, allowing fuel to flow. Since the injector flow orifice is fixed and the fuel pressure drop across the injector tip is constant, fuel flow to the engine is regulated by how long the solenoid is energized. Atomization is obtained at the director/metering plate. ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- "Integral" is a typo in the diagram; it's an "intake" or inlet filter which is easily removed & replaced with a kit like this one. ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Any single injector (MAF or bench) should measure 13-15 Ohms; a bank of 3 (6-cyl MAP) should measure 4-5 Ohms; a bank of 4 (V8 MAP) should measure 3-3.5 Ohms. See also:  .  .  . 
|
|
|
 FuelTank92-95CV.JPG | Hits: 5157 | Size: 57.94 KB | Posted on: 9/20/10 | Link to this image FuelTank92-95CV.JPG | Hits: 5157 | Size: 57.94 KB | Posted on: 9/20/10 | Link to this image
Fuel Tanks for '92-95 CV/GM/TC
Legend for '95 diagrams:
1 Fuel Tank 9002
2 Pin (2 Req'd) N802429-S100
3 Underbody
4 Fuel Tank Support Strap 9092
5 Nut (2 Req'd) N800478-S190
6 Fuel Tank Support 9053
7 Bolt (2 Req'd) N801111-S190
8 Evaporative Emission Tube Shut Off Valve 9G332
9 Evaporative Emission Valve 9B593
10 Fuel Tank Filler Pipe 9034
11 Fuel Tank Filler Pipe Retainer 9B233
12 Screw (4 Req'd) N805402-S56
13 Fuel Tank Filler Cap 9030
14 Fuel Filler Housing
15 Fuel Tank Filler Pipe Sensing Tube Hose
16 Screw W611621-S56
17 Vapor Supply Line
18 Screw (4 Req'd) N610957-S56
A Tighten to 2.3-3.3 N-m (21-29 Lb-In)
B Tighten to 6.8-9.2 N-m (61-81 Lb-In)
|
|
|
 Fuel System Components.jpg | Hits: 5687 | Size: 60.71 KB | Posted on: 2/13/05 | Link to this image Fuel System Components.jpg | Hits: 5687 | Size: 60.71 KB | Posted on: 2/13/05 | Link to this image
Fuel system 2000 CV, GM, TC
|
|
|
 SpringLock Coupling.jpg | Hits: 7891 | Size: 49.68 KB | Posted on: 3/19/05 | Link to this image SpringLock Coupling.jpg | Hits: 7891 | Size: 49.68 KB | Posted on: 3/19/05 | Link to this image
The spring lock coupling is a fuel line coupling held together by a garter spring inside a circular cage. When the coupling is connected together, the flared end of the female fitting slips behind the garter spring inside the cage of the male fitting. The garter spring and cage then prevent the flared end of the male fitting from pulling out of the cage. As a redundant locking feature, a horseshoe shaped retaining clip is incorporated to improve the retaining reliability of the spring lock coupling.
Removal
1. Release fuel system pressure. Refer to «Section 10-01» for fuel system pressure relief procedures. A pressure relief (Schrader) valve on the fuel rail assembly is provided for this procedure.
2. Remove retaining clip from spring lock coupling by hand only. Do not use any sharp tool or screwdriver as it may damage the spring lock coupling.
3. Twist fitting to free it from any adhesion at the O-ring seals.
4. Fit Spring Lock Coupling Disconnect Tool D87L-9280-A (3/8 inch) or D87L-9280-B (1/2 inch) or equivalent to coupling.
5. Close tool and push into open side of cage to expand garter spring and release female fitting.
6. After garter spring is expanded, pull fittings apart.
7. Remove tool from disconnected coupling.
Installation
1. Ensure that garter spring is in cage of male fitting. If garter spring is missing, install a new spring by pushing it into cage opening. If garter spring is damaged, remove it from cage with a small wire hook (do not use a screwdriver) and install a new spring.
2. Clean all dirt or foreign material from both pieces of coupling.
3. Replace missing or damaged O-rings. Use only O-rings listed in Spring Lock Coupling illustration.
WARNING:
USE ONLY THE SPECIFIED O-RINGS AS THEY ARE MADE OF A SPECIAL MATERIAL. THE USE OF ANY O-RING OTHER THAN THE SPECIFIED O-RING MAY ALLOW THE CONNECTION TO LEAK INTERMITTENTLY DURING VEHICLE OPERATION.
Lubricate male fitting and O-rings and inside of female fitting with clean engine oil meeting Ford specification WSE-M2C903-AZ (10W-30) or equivalent.
4. Fit female fitting to male fitting and push until garter spring snaps over flared end of female fitting.
5. Ensure coupling engagement by pulling on fitting and visually checking to ensure garter spring is over flared end of female fitting.
6. Position retaining clip over metal portion of spring lock coupling. Firmly push retaining clip onto spring lock coupling. Ensure that horseshoe portion of clip is over the coupling. Do not install retaining clip over rubber fuel line.
NOTE:
All vehicles require the large, black clip to be installed on the supply side fuel line and the small, gray clip to be installed on the return side fuel line.
|
|
|
 Fuel Pressures.jpg | Hits: 3322 | Size: 37.93 KB | Posted on: 3/20/05 | Link to this image Fuel Pressures.jpg | Hits: 3322 | Size: 37.93 KB | Posted on: 3/20/05 | Link to this image
Fuel Pressures
NOTE:
Maximum fuel pressure is obtainable at WOT or the vacuum hose removed from the fuel pressure regulator.
|
|
|
FPR
The fuel pressure regulator is attached to the fuel supply manifold assembly downstream of the fuel injectors. It regulates the fuel pressure supplied to the injectors. The regulator is a diaphragm-operated relief valve in which one side of the diaphragm senses fuel pressure and the other side is subjected to intake manifold vacuum. The nominal fuel pressure is established by a spring preload applied to the diaphragm. Balancing one side of the diaphragm with manifold pressure maintains a constant fuel pressure drop across the injectors.
Excess fuel is bypassed through the regulator and returns to the fuel tank.
|
|
|
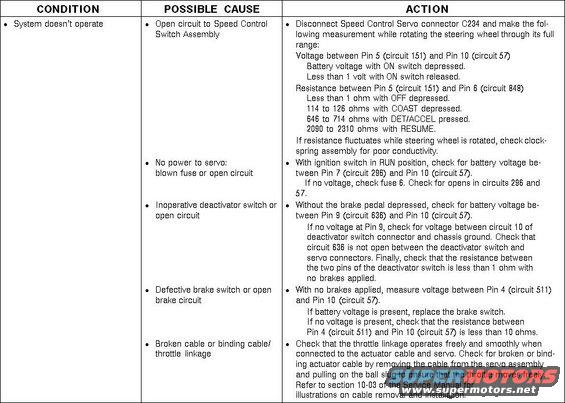 CruiseDiagnosticsElectronic.jpg | Hits: 3489 | Size: 58.21 KB | Posted on: 2/12/05 | Link to this image CruiseDiagnosticsElectronic.jpg | Hits: 3489 | Size: 58.21 KB | Posted on: 2/12/05 | Link to this image
Cruise Control Diagnostics for electronic servo system
|
|
|
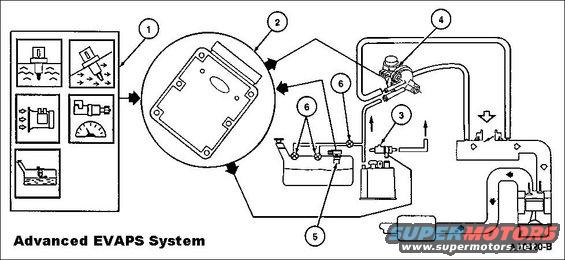 AdvancedEvapsSystem.jpg | Hits: 12276 | Size: 37.44 KB | Posted on: 3/20/05 | Link to this image AdvancedEvapsSystem.jpg | Hits: 12276 | Size: 37.44 KB | Posted on: 3/20/05 | Link to this image
The EVAP Running Loss system consists of a fuel tank, fuel filler cap, fuel tank mounted or in-line fuel vapor control valve, fuel vapor vent valve EVAP canister, fuel tank pressure (FTP) sensor, EVAP canister purge valve, intake manifold hose assembly, canister vent (CV) solenoid, powertrain control module (PCM) and connecting wires and fuel vapor hoses.
1. The EVAP Running Loss system uses inputs from the engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor, the intake air temperature (IAT) sensor, the mass air flow (MAF) sensor, the vehicle speed sensor (VSS) and the fuel tank pressure (FTP) sensor to provide information about engine operating conditions to the PCM. The fuel level input (FLI) and FTP sensor signals to the PCM are used by the PCM to determine activation of the EVAP Monitor based on presence of vapor generation or fuel sloshing.
2. The PCM calculates a variable duty cycle based on the desired amount of purge vapor flow to the intake manifold for a given engine condition. The PCM can then output the correct duty cycle to the EVAP canister purge valve. The PCM uses the EVAP Running Loss system inputs to evacuate the system using the EVAP canister purge valve, seals the EVAP Running Loss system from atmosphere using the CV solenoid, and uses the FTP sensor to observe total vacuum lost for a period of time.
3. The canister vent (CV) solenoid seals the EVAP Running Loss system to atmosphere during the EVAP Running Loss Monitor.
4. The PCM outputs a variable duty cycle signal (between 0% and 100%) to the solenoid on the EVAP canister purge valve.
5. The fuel tank pressure (FTP) sensor monitors the fuel tank pressure during engine operation and continuously transmits an input signal to the PCM. During the EVAP monitor testing, the FTP sensor monitors the fuel tank pressure or vacuum build-up.
6. The fuel tank mounted fuel vapor vent valve assembly, fuel tank mounted fuel vapor control valve (or remote fuel vapor control valve) are used in the EVAP Running Loss system to control the flow of fuel vapor entering the engine. All of these valves also prevent fuel tank overfilling during refueling operation and prevent liquid fuel from entering the EVAP canister and the EVAP canister purge valve under any vehicle severe handling or rollover condition. The liquid/vapor fuel discriminator is part of the fuel vapor control valve assembly on Escort/Tracer (2V) applications.
7. The EVAP Running Loss system, including all the fuel vapor hoses, can be checked when a leak is detected by the PCM. This can be done by pressurizing the system using Rotunda Evaporative Emission Tester kit 134-00056 or equivalent and the leak frequency (ultra-sonic) detector included with the kit.
The Fuel Tank Vapor System -
Gasoline is extremely volatile in almost all environments, and even diesel is aromatic. Since these vapors can be flammable or noxious, they must be contained & routed to the engine to be burned. But they are produced even when the vehicle is unused for long periods, so a simple tube from the fuel tank to the engine would still allow them to vent out the air filter. Also, during hot weather or violent maneuvers, the quantity of vapor generated can exceed the engine's capacity at low RPM, so the vapors must be stored & their flow regulated.
The system begins in the fuel tank where one or more valves are used to vent vapor pressure, but also to exclude liquid from the vapor system due to overfilling, slosh, or rollover. There may also be a pressure sensor to monitor the system's operation & effectiveness, and/or a vent valve (CANV solenoid, or built into the cap) to allow fresh air [b]into[/b] the fuel tank or vapor system. As vapor exits the tank, it flows thru a tube to a canister containing carbon (activated charcoal), which absorbs the fuel vapor, but allows air to pass. Depending on the size of the fuel tank, there may be several canisters, or a larger canister. Older canisters are vented, but they're known to collect water, so most modern canisters are sealed. Another tube leads from the canister toward the engine's intake, but it may contain a regulator valve (CANP solenoid, or VMV). The vapor system may also combine with the PCV system at this point.
Being virtually a zero-maintenance system, most faults are simple valve failures, hose leaks, or mechanical damage (collision, road debris, etc.).
Faults in the evaporative systems are usually detected by the use of a special machine which pumps a non-toxic non-flammable high-visibility smoke into the vapor lines to make leaks evident. But a common source of evaporative codes on '97-04 vehicles is the operator not securing the fuel filler cap. Earlier vehicles didn't detect this, and later vehicles are designed to exclude this from turning on the CEL.
|
|
|
Fuel Vapor & Rollover Valve
The Fuel Tank Vapor System -
Gasoline is extremely volatile in almost all environments, and even diesel is aromatic. Since these vapors can be flammable or noxious, they must be contained & routed to the engine to be burned. But they are produced even when the vehicle is unused for long periods, so a simple tube from the fuel tank to the engine would still allow them to vent out the air filter. Also, during hot weather or violent maneuvers, the quantity of vapor generated can exceed the engine's capacity at low RPM, so the vapors must be stored & their flow regulated.
The system begins in the fuel tank where one or more valves are used to vent vapor pressure, but also to exclude liquid from the vapor system due to overfilling, slosh, or rollover. There may also be a pressure sensor to monitor the system's operation & effectiveness, and/or a vent valve (CANV solenoid, or built into the cap) to allow fresh air [b]into[/b] the fuel tank or vapor system. As vapor exits the tank, it flows thru a tube to a canister containing carbon (activated charcoal), which absorbs the fuel vapor, but allows air to pass. Depending on the size of the fuel tank, there may be several canisters, or a larger canister. Older canisters are vented, but they're known to collect water, so most modern canisters are sealed. Another tube leads from the canister toward the engine's intake, but it may contain a regulator valve (CANP solenoid, or VMV). The vapor system may also combine with the PCV system at this point.
Being virtually a zero-maintenance system, most faults are simple valve failures, hose leaks, or mechanical damage (collision, road debris, etc.).
Faults in the evaporative systems are usually detected by the use of a special machine which pumps a non-toxic non-flammable high-visibility smoke into the vapor lines to make leaks evident. But a common source of evaporative codes on '97-04 vehicles is the operator not securing the fuel filler cap. Earlier vehicles didn't detect this, and later vehicles are designed to exclude this from turning on the CEL.
|
|
|
 VaporMgmtValve.jpg | Hits: 3294 | Size: 30.71 KB | Posted on: 12/4/04 | Link to this image VaporMgmtValve.jpg | Hits: 3294 | Size: 30.71 KB | Posted on: 12/4/04 | Link to this image
Vapor Management Valve (VMV)
The Fuel Tank Vapor System -
Gasoline is extremely volatile in almost all environments, and even diesel is aromatic. Since these vapors can be flammable or noxious, they must be contained & routed to the engine to be burned. But they are produced even when the vehicle is unused for long periods, so a simple tube from the fuel tank to the engine would still allow them to vent out the air filter. Also, during hot weather or violent maneuvers, the quantity of vapor generated can exceed the engine's capacity at low RPM, so the vapors must be stored & their flow regulated.
The system begins in the fuel tank where one or more valves are used to vent vapor pressure, but also to exclude liquid from the vapor system due to overfilling, slosh, or rollover. There may also be a pressure sensor to monitor the system's operation & effectiveness, and/or a vent valve (CANV solenoid, or built into the cap) to allow fresh air [b]into[/b] the fuel tank or vapor system. As vapor exits the tank, it flows thru a tube to a canister containing carbon (activated charcoal), which absorbs the fuel vapor, but allows air to pass. Depending on the size of the fuel tank, there may be several canisters, or a larger canister. Older canisters are vented, but they're known to collect water, so most modern canisters are sealed. Another tube leads from the canister toward the engine's intake, but it may contain a regulator valve (CANP solenoid, or VMV). The vapor system may also combine with the PCV system at this point.
Being virtually a zero-maintenance system, most faults are simple valve failures, hose leaks, or mechanical damage (collision, road debris, etc.).
Faults in the evaporative systems are usually detected by the use of a special machine which pumps a non-toxic non-flammable high-visibility smoke into the vapor lines to make leaks evident. But a common source of evaporative codes on '97-04 vehicles is the operator not securing the fuel filler cap. Earlier vehicles didn't detect this, and later vehicles are designed to exclude this from turning on the CEL.
|
|
|
Carbon Canister
The Fuel Tank Vapor System -
Gasoline is extremely volatile in almost all environments, and even diesel is aromatic. Since these vapors can be flammable or noxious, they must be contained & routed to the engine to be burned. But they are produced even when the vehicle is unused for long periods, so a simple tube from the fuel tank to the engine would still allow them to vent out the air filter. Also, during hot weather or violent maneuvers, the quantity of vapor generated can exceed the engine's capacity at low RPM, so the vapors must be stored & their flow regulated.
The system begins in the fuel tank where one or more valves are used to vent vapor pressure, but also to exclude liquid from the vapor system due to overfilling, slosh, or rollover. There may also be a pressure sensor to monitor the system's operation & effectiveness, and/or a vent valve (CANV solenoid, or built into the cap) to allow fresh air [b]into[/b] the fuel tank or vapor system. As vapor exits the tank, it flows thru a tube to a canister containing carbon (activated charcoal), which absorbs the fuel vapor, but allows air to pass. Depending on the size of the fuel tank, there may be several canisters, or a larger canister. Older canisters are vented, but they're known to collect water, so most modern canisters are sealed. Another tube leads from the canister toward the engine's intake, but it may contain a regulator valve (CANP solenoid, or VMV). The vapor system may also combine with the PCV system at this point.
Being virtually a zero-maintenance system, most faults are simple valve failures, hose leaks, or mechanical damage (collision, road debris, etc.).
Faults in the evaporative systems are usually detected by the use of a special machine which pumps a non-toxic non-flammable high-visibility smoke into the vapor lines to make leaks evident. But a common source of evaporative codes on '97-04 vehicles is the operator not securing the fuel filler cap. Earlier vehicles didn't detect this, and later vehicles are designed to exclude this from turning on the CEL.
|
|
|
 CarbonCanisterLines.jpg | Hits: 3282 | Size: 47.12 KB | Posted on: 1/11/05 | Link to this image CarbonCanisterLines.jpg | Hits: 3282 | Size: 47.12 KB | Posted on: 1/11/05 | Link to this image
EVAPS Lines
The Fuel Tank Vapor System -
Gasoline is extremely volatile in almost all environments, and even diesel is aromatic. Since these vapors can be flammable or noxious, they must be contained & routed to the engine to be burned. But they are produced even when the vehicle is unused for long periods, so a simple tube from the fuel tank to the engine would still allow them to vent out the air filter. Also, during hot weather or violent maneuvers, the quantity of vapor generated can exceed the engine's capacity at low RPM, so the vapors must be stored & their flow regulated.
The system begins in the fuel tank where one or more valves are used to vent vapor pressure, but also to exclude liquid from the vapor system due to overfilling, slosh, or rollover. There may also be a pressure sensor to monitor the system's operation & effectiveness, and/or a vent valve (CANV solenoid, or built into the cap) to allow fresh air [b]into[/b] the fuel tank or vapor system. As vapor exits the tank, it flows thru a tube to a canister containing carbon (activated charcoal), which absorbs the fuel vapor, but allows air to pass. Depending on the size of the fuel tank, there may be several canisters, or a larger canister. Older canisters are vented, but they're known to collect water, so most modern canisters are sealed. Another tube leads from the canister toward the engine's intake, but it may contain a regulator valve (CANP solenoid, or VMV). The vapor system may also combine with the PCV system at this point.
Being virtually a zero-maintenance system, most faults are simple valve failures, hose leaks, or mechanical damage (collision, road debris, etc.).
Faults in the evaporative systems are usually detected by the use of a special machine which pumps a non-toxic non-flammable high-visibility smoke into the vapor lines to make leaks evident. But a common source of evaporative codes on '97-04 vehicles is the operator not securing the fuel filler cap. Earlier vehicles didn't detect this, and later vehicles are designed to exclude this from turning on the CEL.
|
|
|
The octane adjust (OCT ADJ) shorting bar is used to retard spark timing. Removal of the shorting bar from the in-line connector will typically retard spark three degrees. The purpose of the OCT ADJ self-test is to check the state of the OCT ADJ shorting bar. A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) will be present if the shorting bar is removed or if there is an open circuit. The OCT ADJ shorting bar is similar in shape to the SPOUT in-line connector. On some applications the Power Steering Pressure (PS P) circuit will also have a similar shorting bar connector. DO NOT remove the shorting bar unless directed by a Technical Service Bulletin (TSB).
|
|
|
The Air Bypass Solenoid (Figures 1, 2 and 3) is used to control engine idle speed and is operated by the Electronic Engine Control (EEC) processor.
Three types of air by-pass valves are released for use (Figures 1, 2 and 3):
> Hitachi (Figure 1)can be identified by a silver metal housing. It can be cleaned. (Refer to Service Manual).
> Hitachi(Figure 2) can be identified by an external vent/filter. It cannot be cleaned.
> Nippondenso (Figure 3) can be identified by a black plastic housing. Do not use cleaning solvent on this valve. To service this valve, replace it.
The valve allows air to bypass the throttle plates and controls:
> Cold engine fast idle
> No touch start
> Dashpot
> Over temperature idle boost
> Engine idle load correction
|
|
|
 Firing Order 94.jpg | Hits: 9762 | Size: 87.92 KB | Posted on: 5/23/05 | Link to this image Firing Order 94.jpg | Hits: 9762 | Size: 87.92 KB | Posted on: 5/23/05 | Link to this image
Firing Order & Plug Wire Routing
|
|
|
The Secondary Air Injection (AIR) System Monitor is an on-board strategy designed to monitor the proper function of the secondary air injection system. The AIR Monitor for the Belt-Driven Secondary Air Injection Pump system consists of two Output State Monitor configurations in the powertrain control module (PCM); one circuit monitors the electrical circuit of the secondary air injection (AIR) bypass solenoid, the second circuit monitors the electrical circuit of the secondary air injection (AIR) diverter solenoid. A functional check is also performed that tests the ability of the AIR system to inject air into the exhaust. The functional check relies upon HO2S feedback to determine the presence of air flow. The monitor is enabled during AIR system operation and only after certain base engine conditions are first satisfied. Input is required from the ECT, IAT, and CKP sensors, and the HO2S Monitor must also have passed without a fault detection to enable the AIR Monitor. The AIR Monitor is also activated during on demand self-test.
1.The AIR bypass solenoid circuit is monitored for open and shorted conditions by the AIR Bypass Output State Monitor. The DTCs associated with this test are DTCs P0413 and P0414.
2.The AIR diverter solenoid circuit is monitored for open and shorted conditions by the AIR Diverter Output State Monitor. The DTCs associated with this test are DTCs P0416 and P0417.
3.An upstream and downstream functional air flow test is performed during idle, once per engine start-up, and only after all HO2S Monitor tests have been successfully performed. The flow test relies upon the upstream and downstream HO2S to detect the presence of additional air in the exhaust when introduced by the Secondary Air Injection system. The DTCs associated with this test are DTCs P0411 and P1411.
4. The MIL is activated after one of the above tests fail on two consecutive drive cycles.
|
|
|
EVR Testing: vacuum should vent from the green line (supply port) on a good valve NOT energized. When energized, vacuum should hold from the black (source port) to the green (closer to the electrical connector).  Resistance across the terminals should be 20-70 ohms. For smallblock trucks, see: 
|
|
|
Exhaust 1993
Exhaust System Alignment
1. Raise and support the vehicle.
2. Check for loose, damaged, or missing heat shields. Install new heat shields as necessary. Check for any trapped foreign material between the heat shields and the exhaust system components.
3. Loosen all exhaust component fasteners and clamps from the exhaust manifolds to muffler inlet pipe.
4. NOTE: Make sure the exhaust insulators are free to move. Beginning at the front of the vehicle, align the exhaust system to establish the maximum clearance. Make sure the muffler extension pipe and the muffler inlet pipe are pushed all the way into the preceding pipe and the notches are correctly lined up with the tabs.
5. Beginning at the front of the vehicle, tighten all fasteners and clamps to specification.
6. Start the engine and check the exhaust system for leaks.
|
|
|
Exhaust 1994
Exhaust System Alignment
1. Raise and support the vehicle.
2. Check for loose, damaged, or missing heat shields. Install new heat shields as necessary. Check for any trapped foreign material between the heat shields and the exhaust system components.
3. Loosen all exhaust component fasteners and clamps from the exhaust manifolds to muffler inlet pipe.
4. NOTE: Make sure the exhaust insulators are free to move. Beginning at the front of the vehicle, align the exhaust system to establish the maximum clearance. Make sure the muffler extension pipe and the muffler inlet pipe are pushed all the way into the preceding pipe and the notches are correctly lined up with the tabs.
5. Beginning at the front of the vehicle, tighten all fasteners and clamps to specification.
6. Start the engine and check the exhaust system for leaks.
|
|
|
Exhaust 95-97
I goofed the header in the image - of course, the exhaust changed in 1998 with Watts-Link rear suspension.
Exhaust System Alignment
1. Raise and support the vehicle.
2. Check for loose, damaged, or missing heat shields. Install new heat shields as necessary. Check for any trapped foreign material between the heat shields and the exhaust system components.
3. Loosen all exhaust component fasteners and clamps from the exhaust manifolds to muffler inlet pipe.
4. NOTE: Make sure the exhaust insulators are free to move. Beginning at the front of the vehicle, align the exhaust system to establish the maximum clearance. Make sure the muffler extension pipe and the muffler inlet pipe are pushed all the way into the preceding pipe and the notches are correctly lined up with the tabs.
5. Beginning at the front of the vehicle, tighten all fasteners and clamps to specification.
6. Start the engine and check the exhaust system for leaks.
|
|
|
Self-Test Jumper for EEC-IV
For more info, see this & the link in its caption:

|
|
|
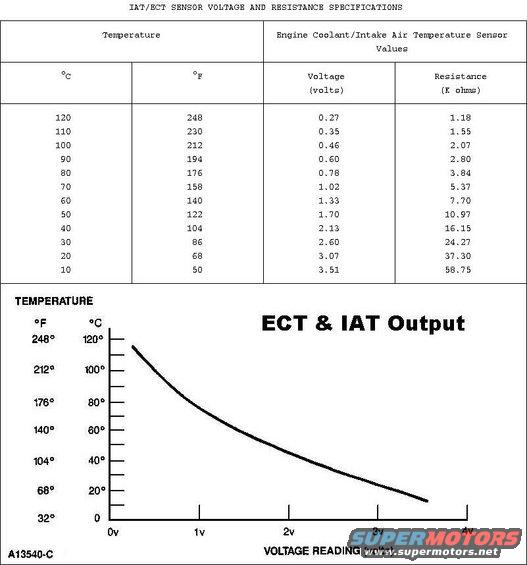 ECT-IAT Output.jpg | Hits: 4634 | Size: 38.08 KB | Posted on: 3/11/05 | Link to this image ECT-IAT Output.jpg | Hits: 4634 | Size: 38.08 KB | Posted on: 3/11/05 | Link to this image
ECT & IAT Output
|
|
|
CHT PID expected values for switching EECs.
The cylinder head temperature (CHT) sensor is a thermistor device in which resistance changes with temperature. The electrical resistance of a thermistor decreases as temperature increases, and increases as temperature decreases. The varying resistance affects the voltage drop across the sensor terminals and provides electrical signals to the PCM corresponding to temperature.
Thermistor-type sensors are considered passive sensors. A passive sensor is connected to a voltage divider network so that varying the resistance of the passive sensor causes a variation in total current flow.
Voltage that is dropped across a fixed resistor in series with the sensor resistor determines the voltage signal at the PCM. This voltage signal is equal to the reference voltage minus the voltage drop across the fixed resistor.
The cylinder head temperature (CHT) sensor is installed in the aluminum cylinder head and measures the metal temperature. The CHT sensor can provide complete engine temperature information and can be used to infer coolant temperature. If the CHT sensor conveys an overheating condition to the PCM, the PCM would then initiate a fail-safe cooling strategy based on information from the CHT sensor. A cooling system failure such as low coolant or coolant loss could cause an overheating condition. As a result, damage to major engine components could occur. Using both the CHT sensor and fail-safe cooling strategy, the PCM prevents damage by allowing air cooling of the engine and limp home capability. For additional information, refer to Powertrain Control Software for Fail-Safe Cooling Strategy details.
Fail-Safe Cooling Strategy
The fail-safe cooling strategy is activated by the PCM only in the event that an overheating condition has been identified. This strategy provides engine temperature control when the cylinder head temperature exceeds certain limits. The cylinder head temperature is measured by the Cylinder Head Temperature (CHT) sensor. For additional information about the CHT sensor, refer to PCM Inputs for a description of the CHT sensor. Note: Not all vehicles equip with a CHT sensor will have the fail-safe cooling strategy.
A cooling system failure such as low coolant or coolant loss could cause an overheating condition. As a result, damage to major engine components could occur. Along with a CHT sensor, the fail-safe cooling strategy is used to prevent damage by allowing air cooling of the engine. This strategy allows the vehicle to be driven safely for a short time with some loss of performance when an overheat condition exist.
Engine temperature is controlled by varying and alternating the number of disabled fuel injectors. This allows all cylinders to cool. When the fuel injectors are disabled, their respective cylinders work as air pumps, and this air is used to cool the cylinders. The more fuel injectors that are disabled, the cooler the engine runs, but the engine has less power.
Note: A wide open throttle (WOT) delay is incorporated if the CHT temperature is exceeded during WOT operation. At WOT, the injectors will function for a limited amount of time allowing the customer to complete a passing maneuver.
Before injectors are disabled, the fail-safe cooling strategy alerts the customer to a cooling system problem by moving the instrument cluster temperature gauge to the hot zone and a PCM DTC P1285 is set. Depending on the vehicle, other indicators, such as an audible chime or warning lamp, can be used to alert the customer of fail-safe cooling. If overheating continues, the strategy begins to disable the fuel injectors, a DTC P1299 is stored in the PCM memory, and a malfunction indicator light (MIL) (either CHECK ENGINE or SERVICE ENGINE SOON), comes on. If the overheating condition continues and a critical temperature is reached, all fuel injectors are turned off and the engine is disabled.
|
|
|
 CHT Sensor Graph.JPG | Hits: 7774 | Size: 36.03 KB | Posted on: 12/4/04 | Link to this image CHT Sensor Graph.JPG | Hits: 7774 | Size: 36.03 KB | Posted on: 12/4/04 | Link to this image
CHT Sensor Graph for switching EECs
The cylinder head temperature (CHT) sensor is a thermistor device in which resistance changes with temperature. The electrical resistance of a thermistor decreases as temperature increases, and increases as temperature decreases. The varying resistance affects the voltage drop across the sensor terminals and provides electrical signals to the PCM corresponding to temperature.
Thermistor-type sensors are considered passive sensors. A passive sensor is connected to a voltage divider network so that varying the resistance of the passive sensor causes a variation in total current flow.
Voltage that is dropped across a fixed resistor in series with the sensor resistor determines the voltage signal at the PCM. This voltage signal is equal to the reference voltage minus the voltage drop across the fixed resistor.
The cylinder head temperature (CHT) sensor is installed in the aluminum cylinder head and measures the metal temperature. The CHT sensor can provide complete engine temperature information and can be used to infer coolant temperature. If the CHT sensor conveys an overheating condition to the PCM, the PCM would then initiate a fail-safe cooling strategy based on information from the CHT sensor. A cooling system failure such as low coolant or coolant loss could cause an overheating condition. As a result, damage to major engine components could occur. Using both the CHT sensor and fail-safe cooling strategy, the PCM prevents damage by allowing air cooling of the engine and limp home capability. For additional information, refer to Powertrain Control Software for Fail-Safe Cooling Strategy details.
Fail-Safe Cooling Strategy
The fail-safe cooling strategy is activated by the PCM only in the event that an overheating condition has been identified. This strategy provides engine temperature control when the cylinder head temperature exceeds certain limits. The cylinder head temperature is measured by the Cylinder Head Temperature (CHT) sensor. For additional information about the CHT sensor, refer to PCM Inputs for a description of the CHT sensor. Note: Not all vehicles equip with a CHT sensor will have the fail-safe cooling strategy.
A cooling system failure such as low coolant or coolant loss could cause an overheating condition. As a result, damage to major engine components could occur. Along with a CHT sensor, the fail-safe cooling strategy is used to prevent damage by allowing air cooling of the engine. This strategy allows the vehicle to be driven safely for a short time with some loss of performance when an overheat condition exist.
Engine temperature is controlled by varying and alternating the number of disabled fuel injectors. This allows all cylinders to cool. When the fuel injectors are disabled, their respective cylinders work as air pumps, and this air is used to cool the cylinders. The more fuel injectors that are disabled, the cooler the engine runs, but the engine has less power.
Note: A wide open throttle (WOT) delay is incorporated if the CHT temperature is exceeded during WOT operation. At WOT, the injectors will function for a limited amount of time allowing the customer to complete a passing maneuver.
Before injectors are disabled, the fail-safe cooling strategy alerts the customer to a cooling system problem by moving the instrument cluster temperature gauge to the hot zone and a PCM DTC P1285 is set. Depending on the vehicle, other indicators, such as an audible chime or warning lamp, can be used to alert the customer of fail-safe cooling. If overheating continues, the strategy begins to disable the fuel injectors, a DTC P1299 is stored in the PCM memory, and a malfunction indicator light (MIL) (either CHECK ENGINE or SERVICE ENGINE SOON), comes on. If the overheating condition continues and a critical temperature is reached, all fuel injectors are turned off and the engine is disabled.
Note: Not all vehicles with a cylinder head temperature (CHT) sensor have the fail-safe cooling strategy. But most with ONLY an electric cooling fan motor (not those with both electric AND pulley-driven) have FSC.
|
|
|
The heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) detects the presence of oxygen in the exhaust and produces a variable voltage according to the amount of oxygen detected. A high concentration of oxygen (lean air/fuel ratio) in the exhaust produces a low voltage signal less than 0.4 volt. A low concentration of oxygen (rich air/fuel ratio) produces a high voltage signal greater than 0.6 volt. The HO2S provides feedback to the PCM indicating air/fuel ratio in order to achieve a near stoichiometric air/fuel ratio of 14.7:1 during closed loop engine operation. The HO2S generates a voltage between 0.0 and 1.1 volts. Embedded with the sensing element is the HO2S heater. The heating element heats the sensor to temperatures of 800°C (1400°F). At approximately 300°C (600°F) the engine can enter closed loop operation. The VPWR circuit supplies voltage to the heater and the PCM will complete the ground when the proper conditions occur. For model year 1998 a new HO2S heater and heater control system are installed on some vehicles. The high power heater reaches closed loop fuel control temperatures sooner, regardless of exhaust system temperature. The use of this heater requires that the HO2S heater control be duty cycled, to prevent damage to the heater. The 6 ohm design is not interchangeable with new style 3.3 ohm heater.  My '93 5.8L Bronco uses Bosch HEGO F1UF-9F472-AA (DY-731), 0 258 003 384, 366 16 90, 3 F 16 (probably the date code: 1993 6th month 16th day). My '95 4.9L uses DY-733. To look up other Ford products, enter the VIN or details here: http://www.fordparts.com/ . Then choose the part category, but pay close attention to the notes, because that site doesn't actually sort for the exact vehicle entered.
|
|
|
 Wiring Symbols.jpg | Hits: 6272 | Size: 30.01 KB | Posted on: 12/4/04 | Link to this image Wiring Symbols.jpg | Hits: 6272 | Size: 30.01 KB | Posted on: 12/4/04 | Link to this image
Wiring Symbols
|
|
|
 00CVDashConnectors.jpg | Hits: 4049 | Size: 64.86 KB | Posted on: 12/4/04 | Link to this image 00CVDashConnectors.jpg | Hits: 4049 | Size: 64.86 KB | Posted on: 12/4/04 | Link to this image
Dash Connectors 00 CV
|
|
|
 InstClusters93.jpg | Hits: 3591 | Size: 58.83 KB | Posted on: 9/16/05 | Link to this image InstClusters93.jpg | Hits: 3591 | Size: 58.83 KB | Posted on: 9/16/05 | Link to this image
93 Clusters
|
|
|
 InstCluster93aEVTM.jpg | Hits: 3076 | Size: 69.96 KB | Posted on: 9/16/05 | Link to this image InstCluster93aEVTM.jpg | Hits: 3076 | Size: 69.96 KB | Posted on: 9/16/05 | Link to this image
93 Cluster Analog
|
|
|
 InstClusters94.jpg | Hits: 3422 | Size: 51.54 KB | Posted on: 9/16/05 | Link to this image InstClusters94.jpg | Hits: 3422 | Size: 51.54 KB | Posted on: 9/16/05 | Link to this image
94 Clusters
|
|
|
 InstCluster94eEVTM.jpg | Hits: 2929 | Size: 77.02 KB | Posted on: 9/16/05 | Link to this image InstCluster94eEVTM.jpg | Hits: 2929 | Size: 77.02 KB | Posted on: 9/16/05 | Link to this image
94 Cluster Electronic
|
|
|
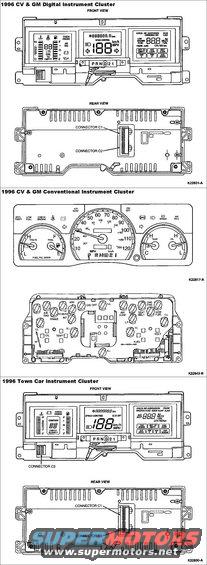 InstClusters96.jpg | Hits: 3500 | Size: 37.49 KB | Posted on: 5/11/05 | Link to this image InstClusters96.jpg | Hits: 3500 | Size: 37.49 KB | Posted on: 5/11/05 | Link to this image
96 Clusters
|
|
|
OBD-II DLC for 2000 GM (C2021F)
|
|
|
 Network Speed Bar Graph.jpg | Hits: 4599 | Size: 29.2 KB | Posted on: 8/31/05 | Link to this image Network Speed Bar Graph.jpg | Hits: 4599 | Size: 29.2 KB | Posted on: 8/31/05 | Link to this image
Network Speeds
ISO9141 - (International Standards Organization) single wire simplex to DLC pin 7 only, strictly for diagnosis, Ford wire colors: LB/Wh
SCP - (Standard Corporate Protocol, J1850) unshielded twisted pair redundant multiplex intermodule, DLC pins 2 & 10, 0-5V, Ford wire colors: SCP Tn/Or; SCP- Pk/LB
CAN - (Controller Area Network) unshielded twisted pair multiplex intermodule 60 Ohm to DLC pins 6 & 14, Ford wire colors: CAN Wh/LG; CAN- Pk/LG
ACP - (Audio Control Protocol) twisted pair ( ASYSON) multiplex, no DLC connection
UBP - single wire multiplex intermodule 12V pulsed to ground
For more info:
|
|
|
 Module Configuration Messages.jpg | Hits: 2734 | Size: 71.02 KB | Posted on: 1/30/05 | Link to this image Module Configuration Messages.jpg | Hits: 2734 | Size: 71.02 KB | Posted on: 1/30/05 | Link to this image
NGS messages during programmable module configuration
|
|
|
 Module Configuration Options.jpg | Hits: 2443 | Size: 17.61 KB | Posted on: 1/30/05 | Link to this image Module Configuration Options.jpg | Hits: 2443 | Size: 17.61 KB | Posted on: 1/30/05 | Link to this image
Programmable module configuration options
|
|
|
The multiplex communication network provides:
> the ability for module-to-module communication by sharing required inputs and outputs instead of each component having an input or output wired directly to or from each affected module.
> a common link for communication to an off-board tester through the data link connector (DLC) located under the instrument panel to the right of the steering column.
The micro-processor based subsystems included on this network are:
> powertrain control
> climate control
> anti-lock brakes
> anti-theft system
A fifth subsystem, the Natural Gas Vehicle (NGV) Module:
> is used only on Crown Victoria Natural Gas Vehicles (NGV).
> utilizes a stand-alone processor to control the fuel indication system (fuel indication is not supported by the multiplex communication network).
> uses the multiplex communication network to communicate with the powertrain control module (PCM) (12A650)
The multiplex communication bus between these subsystems and the data link connector (DLC) consist of an unshielded twisted pair of wires:
> Circuit 914 (T/O) bus(+).
> Circuit 915 (PK/LB) bus(-).
Fault Tolerance: The multiplex communication network will remain operational in the event:
> one circuit is severed.
> one circuit is shorted to ground.
> one circuit is shorted to battery positive voltage (B+).
> a termination resistor is lost within a module.
> one or more modules fail internally.
Any of these conditions will be detected and reported to the off-board tester during diagnostics in the form of a diagnostic trouble code (DTC).
Purpose: The information within this section is designed to diagnose multiplex communication network concerns. These concerns may:
> affect normal functional operations of the vehicle.
> be directly related to customer concerns.
> be undetectable except during diagnostics.
To properly diagnose a network concern, follow the diagnostic procedure outlined in this section in the order presented.
Module Identification: Modules included on this multiplex communication network include:
Powertrain control module
> located in the engine compartment on the passenger side of the dash panel.
> a failure of the communication network to the powertrain control module may result in a no start condition.
> if communication to the powertrain control module fails during diagnosis, refer to Inspection and Verification.
Electronic Automatic Temperature Control (EATC) Module.
> located in the center of the instrument panel.
> loss of communication to powertrain control module may result in degraded automatic temperature control.
> if communication to the electronic automatic temperature control module is lost, refer to «Section 12-03B» for No Communication Testing.
Natural Gas Vehicle (NGV) Module
> natural gas vehicles only.
> located in front of the A/C condenser core (19712) behind the radiator grille.
> if communication to the Natural Gas Vehicle (NGV) Module fails, refer to «Section 13-01C» for No Communication Testing.
Anti-Lock Brake Control Module
> located in the lower LH side of the engine compartment.
> a failed anti-lock brake module (2C219) may cause a no communication condition on the diagnostic communication network.
> if communication to the anti-lock brake module fails, refer to «Section 06-09» for No Communication testing.
Passive Anti-Theft System Control (PATS) Module
> enables and disables vehicle from starting.
> located under left hand side of instrument cluster.
> if communication to the PATS module is lost, refer to «Section 13-11».
|
|
|
The diagnostic communication network:
> consists of a single wire, Circuit 70 (LB/W).
> provides a common link for communication to an off-board tester through the data link connector (DLC) located under the instrument panel (04320) to the right of the steering column.
> does not allow module-to-module communications.
The micro-processor based subsystems included on this network are:
> supplemental air bag system
> keyless entry
> power locks and windows
> interior lighting control
> warning indicator control
Fault Tolerance: The diagnostic communication network will fail if any of the following occur:
> Circuit 70 (LB/W) shorted to ground.
> Circuit 70 (LB/W) shorted to battery positive voltage (B+).
> the module loses power or ground supply.
> a module failure shorts the communication network internally.
Purpose: The information within this section is designed to diagnose any diagnostic communication network concerns. These concerns may:
> affect normal functional operations of the vehicle.
> be directly related to customer concerns.
> be undetectable except during diagnostics.
To properly diagnose a network concern, follow the diagnostic procedure described in this section in the order presented.
Module Identification: Modules included on this diagnostic communication network include:
Electronic Crash Sensor
> located behind the instrument panel to the right of the steering column.
> a failed ECS may cause a no communication condition on the diagnostic communication network.
> if communication to the electronic crash sensor fails, refer to «Section 01-20B» for No Communication testing.
Driver Door Module
> located behind driver front door trim panel (23942).
> if communication to the driver door module fails, refer to «Section 01-11» for No Communication testing.
Lighting Control Module
> located behind the instrument panel to the right of the steering column.
> if communication to the lighting control module fails, refer to «Section 17-01» for No Communication testing.
|
|
|
'98-00 CV/MGM Communications
The vehicle has two module communication networks. The standard corporate protocol (SCP) communication network, which is an unshielded twisted pair cable (data bus plus, Circuit 914 [TN/OG] and data bus minus, Circuit 915 [PK/LB]) and the international standards organization (ISO) 9141 communications network which is a single-wire network(Circuit 70 [LB/W]). Both networks can be connected to the scan tool by one connector called the data link connector (DLC). This makes diagnosis and testing these systems easier by allowing one smart tester to be able to diagnose and control any module on the two networks from one connector. The DLC can be found under the instrument panel between the steering column and the radio.
The ISO 9141 communication network does not permit intermodule communication. When the scan tool communicates to modules on the ISO 9141 communication network, the scan tool must ask for all information; the modules cannot initiate communications.
The SCP communication network will remain operational even with the severing of one of the bus wires. Communications will also continue if one of the bus wires is shorted to ground or battery positive voltage (B ), or if some but not all termination resistors are lost.
Unlike the SCP communication network, the ISO 9141 communication network will not function if the wire is shorted to ground or battery positive voltage (B ). Also, if one of the modules on the ISO 9141 communication network loses power or shorts internally, communications to that module will fail.
For more info:

|
|
|
 Alternator01CV.JPG | Hits: 3510 | Size: 72.49 KB | Posted on: 11/15/10 | Link to this image Alternator01CV.JPG | Hits: 3510 | Size: 72.49 KB | Posted on: 11/15/10 | Link to this image
4G Alternator 01 CV (internal S circuit)
3G, see this:
 . 
4G & 6G see this:

|
|
|
 96 CV Alternator.JPG | Hits: 12135 | Size: 50.94 KB | Posted on: 12/4/04 | Link to this image 96 CV Alternator.JPG | Hits: 12135 | Size: 50.94 KB | Posted on: 12/4/04 | Link to this image
3G Alternator 96 CV Similar to most '87-03 Fords. Ground the F terminal on the voltage regulator BRIEFLY to force the alternator to its max output (voltage & current). Engine RPM should be held above 1500 during the test. See also:  4G & 5G see this: 
|
|
|
Radio 92 Grand Marquis Premium Sound
|
|
|
 Radio 98Premium.jpg | Hits: 2703 | Size: 59.47 KB | Posted on: 8/7/05 | Link to this image Radio 98Premium.jpg | Hits: 2703 | Size: 59.47 KB | Posted on: 8/7/05 | Link to this image
Radio 1998 CV/GM Premium
|
|
|
 PowerWindows96p3.jpg | Hits: 3279 | Size: 66.2 KB | Posted on: 1/9/05 | Link to this image PowerWindows96p3.jpg | Hits: 3279 | Size: 66.2 KB | Posted on: 1/9/05 | Link to this image
96 CV Power Windows p.100-3
|
|
|
Door Locks w/o Keyless Entry or Driver's Door Module (Old-style)
|
|
|
1998 Crown Victoria Door Locks
|
|
|
 Autolamp Circuit.jpg | Hits: 2875 | Size: 19.78 KB | Posted on: 12/4/04 | Link to this image Autolamp Circuit.jpg | Hits: 2875 | Size: 19.78 KB | Posted on: 12/4/04 | Link to this image
Auto Lamps
|
|
|
 Headlight Sw 96CVGM.jpg | Hits: 2965 | Size: 61.44 KB | Posted on: 8/10/05 | Link to this image Headlight Sw 96CVGM.jpg | Hits: 2965 | Size: 61.44 KB | Posted on: 8/10/05 | Link to this image
Headlight Sw 96CVGM
|
|
|
Corner Lamps '98-99 CV/GM
|
|
|
 Headlight Sw 03MM.jpg | Hits: 2777 | Size: 43.59 KB | Posted on: 8/10/05 | Link to this image Headlight Sw 03MM.jpg | Hits: 2777 | Size: 43.59 KB | Posted on: 8/10/05 | Link to this image
Headlight Sw 03CVGMMM
|
|
|
 CompassMirRemove.jpg | Hits: 4504 | Size: 18.31 KB | Posted on: 1/30/05 | Link to this image CompassMirRemove.jpg | Hits: 4504 | Size: 18.31 KB | Posted on: 1/30/05 | Link to this image
Insert a small screwdriver into the slot at the base of the interior rear view mirror. Either push the mirror up along the glass, OR hold the interior rear view mirror and pull the screwdriver rearward until the interior rear view mirror snaps away from the interior rear view bracket. 
|
|
|
Compass Zones
Zone Setting
1. Insert an appropriate diameter rod, preferably non-metallic, into the right switch access hole underneath the compass module and gently press the RH switch for one to two seconds until ZONE and the current zone setting are displayed.
Alternatively, press & hold the COMP button until a numeral is displayed.
2. Release the switch.
3. Pressing the COMP switch repeatedly will cycle the display through all possible zone settings. Stop cycling when the correct zone setting for your location is displayed.
4. Releasing the switch for two seconds will exit the zone setting mode.
Calibration
1. For optimum calibration, switch off all non-essential electrical accessories (rear window defrost, heater/air conditioning, map lamps, wipers, etc.) to make sure all doors are shut.
2. Drive to an open, level area away from large metallic objects or structures with no traffic or pedestrians.
3. Insert an appropriate diameter rod, preferably non-metallic, into the LH switch access hole underneath the compass module and press gently for one to two seconds until CAL and a direction are displayed.
Alternatively, press & hold the COMP button until CAL and a direction are displayed.
4. Release the switch and drive slowly in a circle until CAL disappears from the display (about two to three circles).
|
|
|
Rear-View Electrochromic Mirror with temperature Most GenTex mirrors use this connector, regardless of style & features. Mirrors with fewer features simply delete the applicable wires from the connector, but all should have at least the first 3 wires. WPT-193 Chevy colors are 1 Pk (or Y or Br), 2 Bk, 3 Gn, 4 Gy, 5 LPk, 6 LG/Bk (or DG/W), 7 Br (or Bk/W). Ford colors are 1 Pu/O (or W/LB), 2 Bk, 3 Bk/Pk, 4 Pu, 5 LB/W, 6 Pk/Bk, 7 LB/O. For more info, see this caption: 
|
|
|
 AC System Function.jpg | Hits: 20730 | Size: 44.6 KB | Posted on: 7/24/05 | Link to this image AC System Function.jpg | Hits: 20730 | Size: 44.6 KB | Posted on: 7/24/05 | Link to this image
A/C System Function IF THE IMAGE IS TOO SMALL, click it. The compressor (4) pulls low-temp./press. refrigerant vapor (11) from the accumulator (3) and raises its pressure & temperature. As it flows through the condenser ( 8 ), the refrigerant's higher-than-ambient temperature causes heat to flow out into the airstream, allowing the refrigerant to condense into a high-temp./press. liquid (14). The pressure is a result of the precise restriction caused by the orifice tube (9). As the refrigerant flows slowly through it, the pressure drops suddenly, causing the refrigerant to flash-boil from a low-press. liquid (13) into a low-temp./press. vapor (11). To change from liquid to vapor, the refrigerant must absorb heat through the evaporator, which cools the cabin airstream. The refrigerant then returns to the accumulator where it continues to boil & is dried by a desiccant. If refrigerant leaks out OR the cabin airstream is too cold, the pressure in the evaporator will be too low to keep the cycling switch (2) ON below ~20psi. If the system is overcharged OR the ambient airstream is too hot, pressure in the condenser will cause the pressure cut-off switch (6) to turn OFF above ~400psi. If that fails, then the pressure relief valve (5) will vent refrigerant above ~500psi.  . 
|
|
|
 RDefrost 99CVGM.JPG | Hits: 2968 | Size: 44.43 KB | Posted on: 10/20/06 | Link to this image RDefrost 99CVGM.JPG | Hits: 2968 | Size: 44.43 KB | Posted on: 10/20/06 | Link to this image
Rear Defrost 99 CV GM
|
|
|
 Washer Jet Late.jpg | Hits: 2978 | Size: 28.1 KB | Posted on: 12/4/04 | Link to this image Washer Jet Late.jpg | Hits: 2978 | Size: 28.1 KB | Posted on: 12/4/04 | Link to this image
Washer Jet
The windshield washer system has two windshield washer nozzle jet and brackets (17603) located on the cowl vent screens (018A16).
The washer system is activated by pushing in on the outboard end of the multi-function switch (13K359).
This action energizes a windshield washer pump (17664) mounted inside a cavity in the windshield washer reservoir (17618 ).
The windshield washer reservoir is mounted on the fender apron.
If multi-function switch is in OFF or INT position, windshield wiper will run as long as knob is pushed in. When the knob is released, washers will stop immediately, but windshield wipers will continue to run for three to four cycles before returning to OFF or interval operation.
If the multi-function switch is in LO or HI position, washers operate with no change in windshield wiper operation.
NOTE: The windshield washer nozzle jet and bracket sprays windshield washer fluid in a fan-like pattern onto the windshield glass (03100), but the jet is actually a single oscillating stream. Only actuate the system momentarily to avoid sending more fluid than needed through the system.
The windshield washer nozzle jet and bracket is not adjustable, and is mounted to the cowl vent screens.
|
|
|
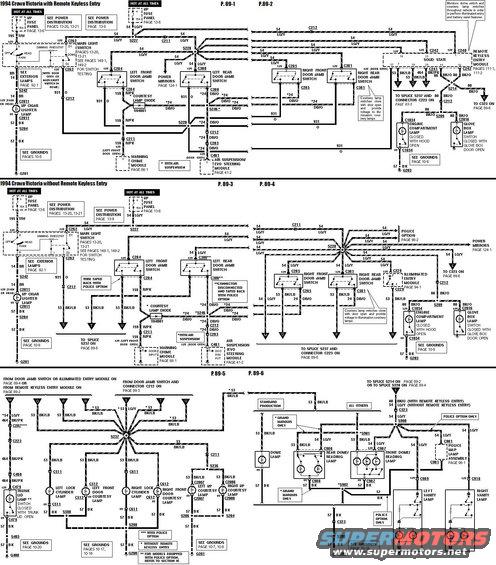 Courtesy Circuit 94.jpg | Hits: 3510 | Size: 88.61 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image Courtesy Circuit 94.jpg | Hits: 3510 | Size: 88.61 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image
Courtesy Circuit 94
|
|
|
 Courtesy Circuit 98.jpg | Hits: 3359 | Size: 48.87 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image Courtesy Circuit 98.jpg | Hits: 3359 | Size: 48.87 KB | Posted on: 1/2/05 | Link to this image
Courtesy Circuit 98
|
|
|
1994 Crown Victoria & Grand Marquis Fuses
|
|
|
1997 Crown Victoria & Grand Marquis Fuses
|
|
|
2000 Crown Victoria & Grand Marquis Fuses
|
|
|
'98 Power Distribution P.13-9
|
|
|
Driver's Door Module for '98 Crown Vic & Grand Marquis.
|
|
|
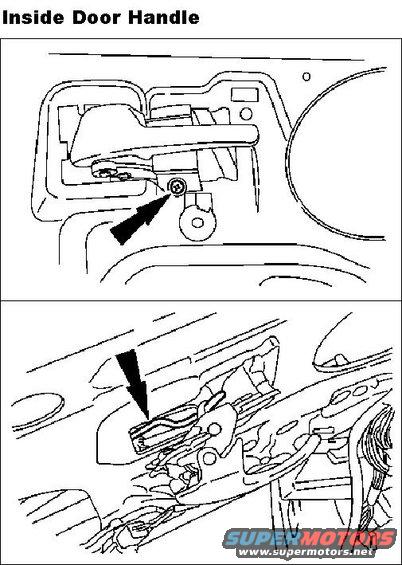 Door Handle Inside.jpg | Hits: 2755 | Size: 61.33 KB | Posted on: 8/23/05 | Link to this image Door Handle Inside.jpg | Hits: 2755 | Size: 61.33 KB | Posted on: 8/23/05 | Link to this image
Inside Door Handle
|
|
|
 DoorLatchFront98.jpg | Hits: 3452 | Size: 82.86 KB | Posted on: 10/18/05 | Link to this image DoorLatchFront98.jpg | Hits: 3452 | Size: 82.86 KB | Posted on: 10/18/05 | Link to this image
Front Door Latch '98
|
|
|
 DoorLatchRear98.jpg | Hits: 5153 | Size: 86.4 KB | Posted on: 10/18/05 | Link to this image DoorLatchRear98.jpg | Hits: 5153 | Size: 86.4 KB | Posted on: 10/18/05 | Link to this image
Rear Door Latch '98
|
|
|
 WindowRegulators.jpg | Hits: 6858 | Size: 78.99 KB | Posted on: 1/14/06 | Link to this image WindowRegulators.jpg | Hits: 6858 | Size: 78.99 KB | Posted on: 1/14/06 | Link to this image
Window Regulator
Front Door
Removal
1. If front door window glass (21410) is in the down position and is inoperable, the following steps must be taken; if front door window glass is operational, go to Step 2.
a. Remove front door trim panel (23942) and front door trim shield (237A04).
b. Disconnect battery ground cable (14301).
c. Disconnect window regulator electric drive harness connector.
d. Remove window regulator electric drive retaining screws through holes.
CAUTION: Be careful not to strike or scratch front door window glass because it can break.
e. Remove window regulator electric drive (23394) from front door power window regulator.
f. Raise front door window glass to full up position by hand and secure with tape.
g. Go to Step 5.
2. Remove front door trim panel and front door trim shield.
3. Remove front door window glass as described.
4. Disconnect window regulator electric drive harness connector.
5. Remove two 1/4-inch rivets retaining lower bracket of front door power window regulator to inner panel. Use drift punch to knock out center pins for each rivet. Using a 1/4-inch diameter drill, drill out remainder of rivet.
Note: Use care not to enlarge sheet metal holes in the door inner panel.
6. Remove three window regulator electric drive retaining screws from inside door to remove window regulator electric drive from front door power window regulator.
7. Remove two window regulator retaining nuts.
8. Remove front door power window regulator from front door (20124).
Installation
1. Lubricate regulator mechanism with Teflon® Lubricant D2AZ-19590-A or equivalent meeting Ford specification ESB-M1C111-A.
2. Install front door power window regulator minus motor (23208 ) into access hole in inner panel.
3. Position front door power window regulator using upper studs and tabs on window regulator electric drive mounting bracket.
4. Install rivets retaining front door power window regulator to door inner panel (1/4-20 x 1/2 inch screw and 1/4-20 nut and washer assemblies or equivalent metric fasteners may be used).
5. Install two upper front door power window regulator retaining nuts.
6. Install window regulator electric drive with three screws. Do not overtighten screws.
7. Install front door window glass.
8. Adjust front door window glass as described.
9. Install front door trim shield and front door trim panel.
Rear Door
Removal
1. If rear door window glass (25712) is in the down position and is inoperable, the following steps must be taken; if rear door window glass is operational, go to Step 2.
CAUTION: When servicing rear door electric window regulator (27008 ) assembly, regulator cable tension must not be altered. Cable tension is preset at production. Improper adjustment can result in premature rear door electric window failure or erratic operation.
a. Remove rear door trim panel (27406) and watershield.
b. Mark inner door panel and drill three 1/2 inch holes as shown
CAUTION: Be careful not to drill through the mechanism behind inner door panel.
CAUTION: Be careful not to strike or scratch rear door window glass (25713) because it can break.
c. Remove rear door electric window regulator retaining screws through holes.
d. Remove rear door electric window regulator from mounting bracket through access hole.
e. Remove window regulator electric drive from housing and cover.
f. Raise rear door window glass to full up position by hand and secure with a clamp.
g. Go to Step 4.
2. Remove rear door trim panel and watershield.
3. Remove rear door window glass as described.
4. Disconnect window regulator electric drive harness connector.
5. Remove three 1/4-inch rivets retaining rear door electric window regulator bracket to inner panel and two 1/4-inch rivets retaining lower bracket of rear door electric window regulator to inner panel. Use drift punch to knock out center pins for each rivet. Using a 1/4-inch diameter drill, drill out remainder of rivet. Use care not to enlarge sheet metal holes in the door inner panel.
6. Remove two upper rear door electric window regulator retaining nuts.
7. Remove rear door electric window regulator.
Rear Door
Installation
1. Lubricate rear door electric window regulator with Teflon® Lubricant D2AZ-19590-A or equivalent meeting Ford specification ESB-M1C111-A.
2. Install rear door electric window regulator into access hole in inner panel.
3. Position rear door electric window regulator using upper rear door electric window regulator studs and tabs on window regulator electric drive mounting bracket.
4. Install rivets retaining rear door electric window regulator to door inner panel (1/4-20 x 1/2 inch bolt and 1/4-20 nut and washer assemblies or equivalent metric fasteners may be used as alternates).
5. Install two upper rear door electric window regulator retaining nuts. Tighten to 9-14 Nm (80-124 lb-in).
6. Install rear door electric window regulator as described.
7. Adjust rear door window glass as described.
8. Install watershield and rear door trim panel.
|
|
|
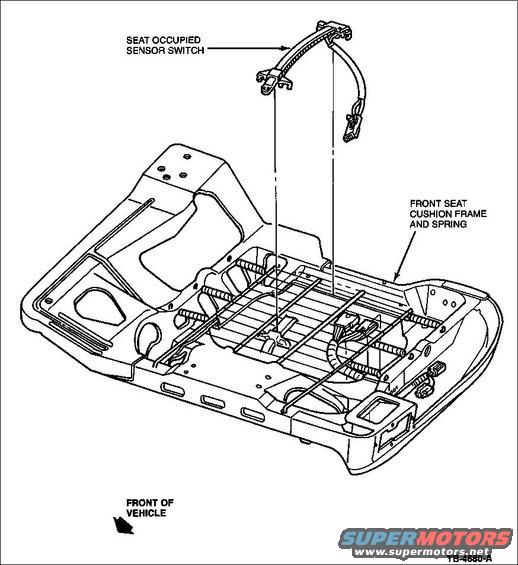 95 CV Seat Base.jpg | Hits: 2903 | Size: 57.8 KB | Posted on: 12/4/04 | Link to this image 95 CV Seat Base.jpg | Hits: 2903 | Size: 57.8 KB | Posted on: 12/4/04 | Link to this image
Seat Base 95 CV
|
|
|
 HeadrestRemoval.jpg | Hits: 2642 | Size: 39.88 KB | Posted on: 3/29/05 | Link to this image HeadrestRemoval.jpg | Hits: 2642 | Size: 39.88 KB | Posted on: 3/29/05 | Link to this image
Headrest Removal 2000
|
|
|
Power Seats 03 Crown Vic & Grand Marquis (not Marauder)
|
|
|
Driver's Memory Seat '06 LTC
|
|
|
 Seat06TC_componentL.JPG | Hits: 2394 | Size: 47.13 KB | Posted on: 9/14/06 | Link to this image Seat06TC_componentL.JPG | Hits: 2394 | Size: 47.13 KB | Posted on: 9/14/06 | Link to this image
Driver's Memory Seat '06 LTC Component View & Connectors
|
|
|
 Seat06TCMem_wiringL.JPG | Hits: 2406 | Size: 74.42 KB | Posted on: 9/14/06 | Link to this image Seat06TCMem_wiringL.JPG | Hits: 2406 | Size: 74.42 KB | Posted on: 9/14/06 | Link to this image
Driver's Memory Seat '06 LTC
|
|
|
DTC 12: LOST BATTERY FEED
Normal Operation
The air bag diagnostic monitor measures the voltage at Pin 14 of the air bag diagnostic monitor connector. Voltage at Pin 14 should be equal to battery voltage. If the voltage at Pin 14 drops to less than 8 volts, the air bag diagnostic monitor will flash out on the air bag indicator a DTC 12. If the voltage at Pin 14 drops to less than 5 volts, the air bag diagnostic monitor will also store a DTC 12 in memory. Should the loss of battery voltage at Pin 14 be intermittent or repaired, the air bag diagnostic monitor will flash out a DTC 52 (or higher priority code if one exists) on the next ignition switch cycle.
Possible Causes
WARNING:
UNDER NO CIRCUMSTANCES SUBSTITUTE ANOTHER FUSE VALUE. ANY FUSE OTHER THAN 10A MAY CAUSE DISARMING FAILURE AND MAY RESULT IN DANGER TO THE OCCUPANTS OF THE VEHICLE. DO NOT ATTEMPT TO REPLACE THE 10A FUSE UNLESS THE AIR BAG SYSTEM FIRST HAS BEEN DEACTIVATED (SEE «DEACTIVATION» PROCEDURE FOR DETAILS).
NOTE:
If a short to ground exists on any of the Circuits 607 (LB/O), 614 (GY/O), 615 (GY/W), or 616 (PK/BK) leading to a DTC 13 or 53, or similarly a short to ground exists on any of Circuits 617 (PK/O), 619 (PK/W), 624 (Y/W), 625 (Y/LG) leading to a DTC 14 or 54, the air bag diagnostic monitor will activate a solid state switch at Pin 13 of the air bag diagnostic monitor. This causes the 10 amp battery fuse to blow, thus disarming the air bag system and preventing inadvertent air bag deployment. If the 10 amp fuse junction panel (or power distribution in some vehicles) battery fuse has blown, it must be replaced by a 10A fuse.
Low voltage at air bag diagnostic monitor Pin 14 can be caused by:
> An open in the battery circuit that would prevent battery voltage from reaching air bag diagnostic monitor Pin 14.
After the air bag diagnostic monitor has disarmed the air bag system, it will not be enabled to disarm again until the appropriate condition (DTC 13, 14, 53, or 54) has been serviced and cleared (refer to DTC «13» , «14» , «53» ,and «54» and «Diagnostic Trouble Code Clearing» descriptions for further details).
> A short to ground on the battery feed circuit between the fuse and Pin 13 or Pin 14 of the air bag diagnostic monitor.
> A concern in the charging system causing battery voltage to drop below 8 volts.
|
|
|
 ADM_DTC_Clear95.JPG | Hits: 5737 | Size: 50.36 KB | Posted on: 10/8/06 | Link to this image ADM_DTC_Clear95.JPG | Hits: 5737 | Size: 50.36 KB | Posted on: 10/8/06 | Link to this image
'95 Airbag Code Clearing
Diagnostic Trouble Code Clearing: Procedure to Clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes from Diagnostic Monitor Non-Volatile Random Access Memory.
Normal Operation:
The air bag diagnostic monitor (14B056) continually checks the air bag system for readiness. When a fault condition is detected, the DTC associated with that fault is stored in the air bag diagnostic monitor's Non-Volatile Random Access Memory (NVRAM). After writing the DTC to NVRAM, the air bag diagnostic monitor signals the fault by flashing the appropriate diagnostic trouble code on the air bag indicator.
The diagnostic trouble code written to NVRAM is permanently stored in the air bag diagnostic monitor until cleared by the diagnostic trouble code clearing procedure.
> Upon each cycle of the ignition switch (11572), the air bag diagnostic monitor checks for diagnostic trouble codes written in NVRAM. If any diagnostic trouble codes exist in NVRAM, the air bag diagnostic monitor will then check to see if these fault conditions are still present.
> If the conditions of the diagnostic trouble code in NVRAM are still present, then the air bag diagnostic monitor will use the air bag indicator to flash out the diagnostic trouble code number that was written in memory.
> If the conditions of the diagnostic trouble code are not still present (indicating an intermittent or serviced fault), the air bag diagnostic monitor will use the air bag indicator to flash out a DTC which is the sum of the diagnostic trouble code in NVRAM plus 40.
Example: Due to corrosion, high resistance develops on the driver side air bag circuit. The air bag diagnostic monitor stores a diagnostic trouble code 32 in NVRAM. Upon each cycle of the ignition switch, the air bag diagnostic monitor checks the resistance of the driver air bag circuit.
> If the resistance is still high, the air bag diagnostic monitor causes the air bag indicator to flash out a DTC 32.
> If the resistance falls within the normal range due to service or an intermittent condition, the air bag diagnostic monitor causes DTC 72 to be flashed on the air bag indicator.
Once a fault has been serviced, the associated diagnostic trouble code may be cleared from NVRAM. Only diagnostic trouble codes that the air bag diagnostic monitor sees as repaired or intermittent may be cleared (diagnostic trouble codes 52 and above). In no circumstances can hard fault conditions (diagnostic trouble codes 45 and below) be cleared.
1. Follow the diagnostic procedures as outlined to service the fault condition flashing on the air bag indicator.
2. Cycle the ignition switch to OFF and then to RUN.
3. Observe air bag indicator prove-out (six ± two seconds) followed by diagnostic trouble code (52-85) flashing completely one time.
4. Locate the Diagnostic "Trouble Code Clear" Connector located underneath the glove compartment (06010) containing Circuits 631 (T/R) and 57 (BK).
5. Use a jumper wire to short Circuit 631 (T/R) to Circuit 57 (BK) or to another good ground. This short must be made after the diagnostic trouble code flashes completely one time, but before the warning light stays on continuously.
6. Hold short until air bag diagnostic monitor tone sounds (approximately five seconds).
7. Release short on Circuit 631 (T/R) to Circuit 57 (BK). This short must be released within 25 seconds after the diagnostic monitor tone sounds.
Diagnostic trouble code is now cleared from NVRAM. Next highest priority diagnostic trouble code stored in NVRAM (if one exists) will begin flashing.
|
|
|
 AirbagCodes02.JPG | Hits: 3298 | Size: 63.24 KB | Posted on: 10/19/08 | Link to this image AirbagCodes02.JPG | Hits: 3298 | Size: 63.24 KB | Posted on: 10/19/08 | Link to this image
SRS Airbag Codes for '02 CV
Others similar
|
|
|
 AirbagCodes04.jpg | Hits: 3360 | Size: 55.33 KB | Posted on: 11/25/08 | Link to this image AirbagCodes04.jpg | Hits: 3360 | Size: 55.33 KB | Posted on: 11/25/08 | Link to this image
2004 Airbag Codes by priority
|
|
|
 RearSuspExploded.jpg | Hits: 4255 | Size: 70.57 KB | Posted on: 1/16/05 | Link to this image RearSuspExploded.jpg | Hits: 4255 | Size: 70.57 KB | Posted on: 1/16/05 | Link to this image
Exploded 8.8" Suspension
|
|
|
 RearSuspWattsLink.jpg | Hits: 10621 | Size: 62.49 KB | Posted on: 1/30/05 | Link to this image RearSuspWattsLink.jpg | Hits: 10621 | Size: 62.49 KB | Posted on: 1/30/05 | Link to this image
Watts Link rear suspension '98-10 Panther chassis
1 Stabilizer bar and isolator assembly 5A771
2 Shock absorber 18125
3 Upper arm 5501
4 Lower arm 5538
5 Watts link pivot stud W704883-S428
6 Watts link pivot (Part of 4264) 5T516
7 Lateral arm, LH (Part of 4264) 5808
8 Lateral arm, RH (Part of 4264) 5808
CAUTION: Suspension fasteners are critical parts because they affect performance of vital components and systems and their failure can result in major service expense. New fasteners must be installed with the same part number or an equivalent part if installation is necessary. Do not use a replacement part of lesser quality or substitute design. Torque values must be used as specified during reassembly to make sure of correct retention of these parts. Orientation of the fasteners is also important on all rear suspension arms. Make sure the fasteners are installed in the same direction as they were in when removed.
NOTE: If the Watts link pivot stud or nut is loosened, a new Watts link pivot stud and nut service kit must be installed.
The rear suspension comprises four suspension arms, two shock absorbers, two springs, a stabilizer bar and a lateral arm assembly (Watts link).
The rear suspension arms limit the forward and rearward movement of the rear axle in relation to the frame. Each rear spring is mounted to an upper seat integral with the frame and a lower seat welded to the rear axle housing. To reduce noise and vibration, a rubber isolator is placed between the axle and the spring and another between the spring and frame.
The lateral arm assembly (Watts link) is connected between the rear axle differential housing Watts link pivot and the frame. The lateral arm assembly (Watts link) controls the side-to-side sway of the vehicle.
The rear stabilizer bar and links assembly aids in the control of the suspension travel and restricts body roll.
The rear shock absorbers provide motion and force damping of the rear suspension during suspension travel, jounce and rebound.
|
|
|
 RearSuspEndLinks.jpg | Hits: 2920 | Size: 45.63 KB | Posted on: 1/30/05 | Link to this image RearSuspEndLinks.jpg | Hits: 2920 | Size: 45.63 KB | Posted on: 1/30/05 | Link to this image
Rear sway bar end links '00
|
|
|
 Traction-Lok Diff.jpg | Hits: 2719 | Size: 53.93 KB | Posted on: 1/16/05 | Link to this image Traction-Lok Diff.jpg | Hits: 2719 | Size: 53.93 KB | Posted on: 1/16/05 | Link to this image
Traction-Lok Diff
|
|
|
 DiffCoverSealant.jpg | Hits: 2984 | Size: 46.37 KB | Posted on: 1/16/05 | Link to this image DiffCoverSealant.jpg | Hits: 2984 | Size: 46.37 KB | Posted on: 1/16/05 | Link to this image
Diff Cover Sealant
|
|
|
 RearDiscExploded.jpg | Hits: 3548 | Size: 23.43 KB | Posted on: 1/16/05 | Link to this image RearDiscExploded.jpg | Hits: 3548 | Size: 23.43 KB | Posted on: 1/16/05 | Link to this image
Exploded Rear Disc
|
|
|
E-Brake for '92 Crown Victoria, Grand Marquis, & Town Car
Item Part Number Description
1 Sound Deadener
2 2853 Cable Assy
3 2780 Control Assy
4 2A635 Cable Assy RH
5 2A809 Cable Assy LH
6 2C190 Assy
7 Vacuum Hose From Steering Column Switch
8 ECC Module Bracket
9 Axle Assy
10 16B920 Clip
11 LH Lower Control Arm
12 4A047 Bracket
13 N803585-S2 Bolt (3 Req'd) Tighten to 25-35 N-m (17-25 Lb-Ft)
14 Cowl
15 2A792 Cover
16 Frame
17 2860 Bracket
18 N806900-S2 Bolt
|
|
|
Parking Brake 1998
1 -- Sound Deadener
2 -- Front Parking Brake Cable and Conduit (2853)
3 -- Parking Brake Control (2780)
4 -- Parking Brake Rear Cable and Conduit (RH) (2A635)
5 -- Parking Brake Rear Cable and Conduit (LH) (2A635)
6 -- Rear Brake Anti-Lock Sensor (2C190)
7 -- Parking Brake Release Vacuum Hose (2B653)
8 -- Powertrain Control Module Bracket (12A659)
9 -- Rear Axle Assembly (4006)
10 -- Wire Retainer (16B920)
11 -- Rear Suspension Arm and Bushing (5500)
12 -- Stabilizer Bar Bracket (5486)
13 -- Bolt (3 Required) (N803585-S428 )
14 -- Dash Panel (01610)
15 -- Parking Brake Release Handle (2760)
16 -- Brake Hose Clip (2860)
17 -- Bolt (N806900-S2)
18 -- Front Parking Brake Cable Retainer (2K865)
19 -- Screw
20 -- Screw (2 Required) (N611196-S56)
21-- Clamp
A -- Tighten to 25-35 Nm (19-25 Lb-Ft)
B -- Tighten to 12-17 Nm (107-150 Lb-In)
|
|
|
 ParkBrake98Spec.jpg | Hits: 4403 | Size: 21.5 KB | Posted on: 7/28/05 | Link to this image ParkBrake98Spec.jpg | Hits: 4403 | Size: 21.5 KB | Posted on: 7/28/05 | Link to this image
Park Brake Adjustment
Center parking brake shoe and linings on parking brake support plate and, using an 8-inch micrometer, gauge parking brake shoe and linings to dimensions shown.
|
|
|
 ParkBrakeVacValve.jpg | Hits: 3300 | Size: 74.9 KB | Posted on: 11/7/05 | Link to this image ParkBrakeVacValve.jpg | Hits: 3300 | Size: 74.9 KB | Posted on: 11/7/05 | Link to this image
Parking Brake Vacuum Release
|
|
|
'00 Front suspension
1 5482 Front stabilizer bar
2 5K484 Stabilizer bar link (2 req'd)
3 3105 Front wheel spindle (2 req'd)
4 N620042-S100 Nut (2 req'd)
5 3083 Front suspension upper arm (2 req'd)
6 N808998-S428 Bolt (4 req'd)
7 N806579-S428 Bolt (2 req'd)
8 N805475-S428 Nut (2 req'd)
9 %u2014 Frame
10 N805476-S301 Nut (4 req'd)
11 N811745-S426 Bolt (4 req'd)
12 N808943-S428 Nut (4 req'd)
13 5415 Front spring insulator (2 req'd)
14 5310 Front coil spring (2 req'd)
15 3078 Front suspension lower arm (2 req'd)
16 3020 Front suspension bumper (2 req'd)
17 N808509-S428 Nut (2 req'd)
18 N620468-S60 Nut (2 req'd)
19 W520214-S428 Nut (2 req'd)
|
|
|
 Caliper Bracket Front.jpg | Hits: 2792 | Size: 43.2 KB | Posted on: 2/13/05 | Link to this image Caliper Bracket Front.jpg | Hits: 2792 | Size: 43.2 KB | Posted on: 2/13/05 | Link to this image
Caliper Bracket Bolt Torque
|
|
|
 Tire Metric Size.jpg | Hits: 2542 | Size: 37.31 KB | Posted on: 12/4/04 | Link to this image Tire Metric Size.jpg | Hits: 2542 | Size: 37.31 KB | Posted on: 12/4/04 | Link to this image
Tire Size
|
|
|
 TSB TirePressure.jpg | Hits: 2937 | Size: 46.08 KB | Posted on: 12/4/04 | Link to this image TSB TirePressure.jpg | Hits: 2937 | Size: 46.08 KB | Posted on: 12/4/04 | Link to this image
Tire Pressure/Load
|
|
|
 TSB TirePressureWear.jpg | Hits: 2942 | Size: 74.83 KB | Posted on: 12/4/04 | Link to this image TSB TirePressureWear.jpg | Hits: 2942 | Size: 74.83 KB | Posted on: 12/4/04 | Link to this image
Tire Pressure/Life
|
|
|
WIgwag High Beams using a dual-out flasher
NOTE: Most jurisdictions regulate flashing lights on vehicles, so if you're not authorized to have them, don't modify your lighting.
This circuit adds only 3 common relays, a common SPST switch, a common fuse, & a 2-output flasher to create a safe wigwag hi-beam system withOUT the voltage drop associated with diodes.
The primary lighting load remains on the factory fuse; the load of the auxiliary lights & relays (less than 10A) goes on the fuel pump relay (via the new fuse) so the system can only be active when the engine is running. If the hi-beams are in use when the wigwags are switched on, the low-beams come on steady while the highs flash. Even if the LCM fails, the wigwags will still work. If the bypass (center) relay fails, the hi-beams will operate normally and only the aux. lights will flash. If either wigwag relay fails, its headlight will not flash. If the wigwag flasher fails, the hi-beams will shut off, but the lows will be on.
Note that all 3 relays are connected by their 87a terminals, and the flasher is also connected to all 3, so they could all 4 be mounted as a group near the headlights.
The LCM fuse number is for an '03 CV. The wigwag fuse should be sized for the 2 arrays. If no aux arrays are installed, a 3A fuse is sufficient to power the 3 relays.
NOTE: the arrays are only representative - not detailed.
|
|
|
 01 CV Alternator.JPG | Hits: 4818 | Size: 53.74 KB | Posted on: 12/4/04 | Link to this image 01 CV Alternator.JPG | Hits: 4818 | Size: 53.74 KB | Posted on: 12/4/04 | Link to this image
|
|
|